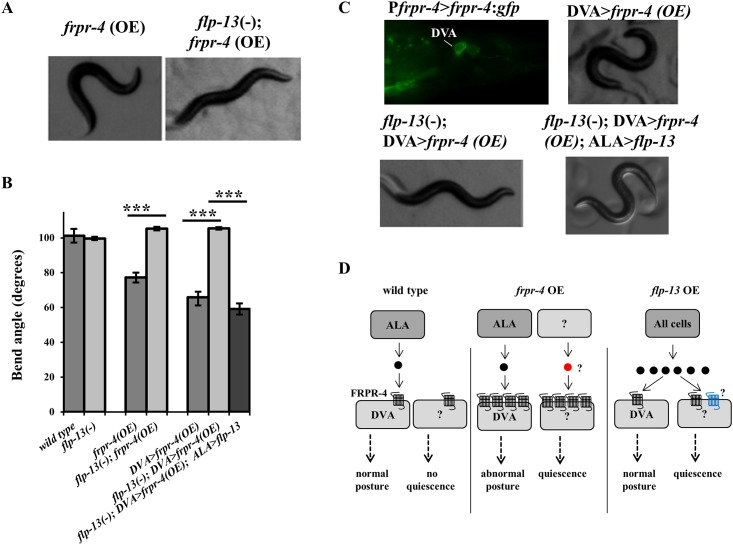
Fig 5. FLP-13 signals through FRPR-4 in DVA to regulate posture.
(A-B) Overexpression of frpr-4 from its endogenous promoter reduces the animals bend angle. The flp-13(tm2427) deletion suppresses this phenotype and expression of flp-13 in the ALA neuron restores this phenotype (Student’s t-test, N>10, ***P < .001). (C) A strain carrying an frpr-4:gfp translational reporter shows GFP localization to the membrane of the DVA neuron. Overexpression of frpr-4 in the DVA neuron using the promoter from the gene twk-16 results in a decrease in bend angle, which is suppressed by the flp-13(tm2427) deletion and then restored by reinstating flp-13 in the ALA neuron. (D) A model of the effects of frpr-4 or flp-13 overexpression on posture and behavioral quiescence. Black circle denote FLP-13 peptides; red circle denotes an unknown peptide. Black seven-transmembrane-domain receptors denote FRPR-4. Blue seven-transmembrane-domain receptors denote an unknown receptor mediating the quiescent effects of FLP-13 peptides.