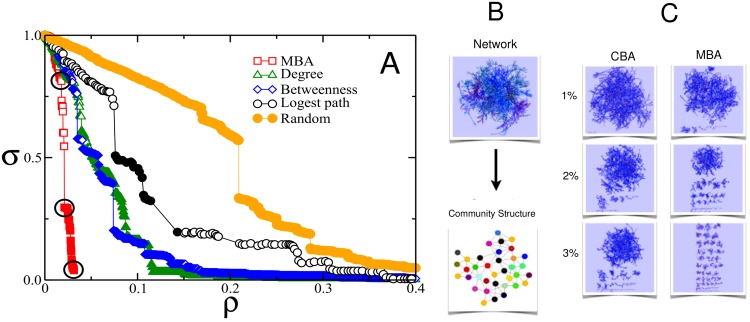
Fig 2. Comparison between the effect of betweenness-based attack, degree-based attack, longest path attack, random attack, and module-based attack for the Western US power grid network.
(A) Size of the biggest connected component in terms of the initial size, σ, as function of fraction of removed nodes, ρ. (B) Network and modular representations of US power grid. (C) Snapshots of the node-representation of the US power grid when 1%, 2% and 3% of nodes are removed using CBA and MBA methods.