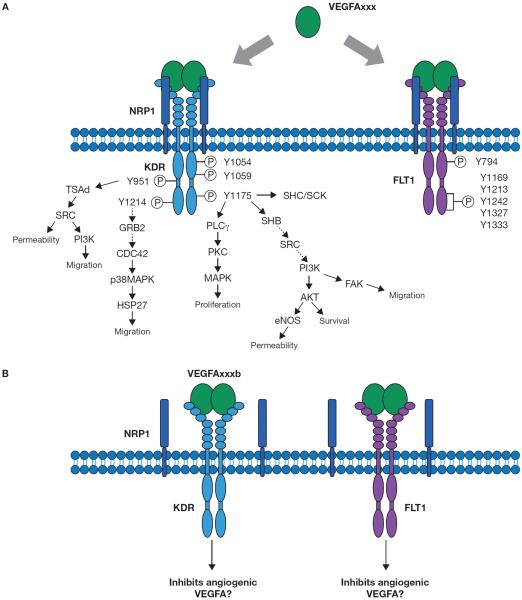
Figure 3.
VEGF receptors which are critical to the actions of VEGFA. Pictured is binding of angiogenic VEGFA isoforms to either KDR (top right) or FLT1 (top left). Only angiogenic isoforms of VEGFA bind to NRP1 (top). Antiangiogenic VEGFA isoform binding to either KDR (bottom left) or FLT1 (bottom right) results in less and different signal transduction than angiogenic. Antiangiogenic VEGFA isoforms are unable to bind NRP1 (bottom). Phosphorylation sties are depicted as “P” within a circle. Y = tyrosine, VEGFA = vascular endothelial growth factor A, KDR = kinase insert domain protein receptor, FLT1 = fms-like tyrosine kinase 1, NRP1 = neuropilin 1, TSAd = T-cell Specific Adaptor, SRC = Rous sarcoma oncogene, PI3K = phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, GRB2 = growth factor receptor bound protein 2, CDC42 = cell division cycle 42, (p38)MAPK = mitogen-activated protein kinase, HSP27 = heat shock protein 27, PLCγ = phospholipase C gamma, PKC = protein kinase C, SHC/SCK = src homology 2 domain-containing transforming protein, SHB = src homology 2 domain-containing transforming protein B, AKT = thymoma viral proto-oncogene, eNOS = nitric oxide synthase 3, endothelial cell, FAK = focal adhesion kinase.