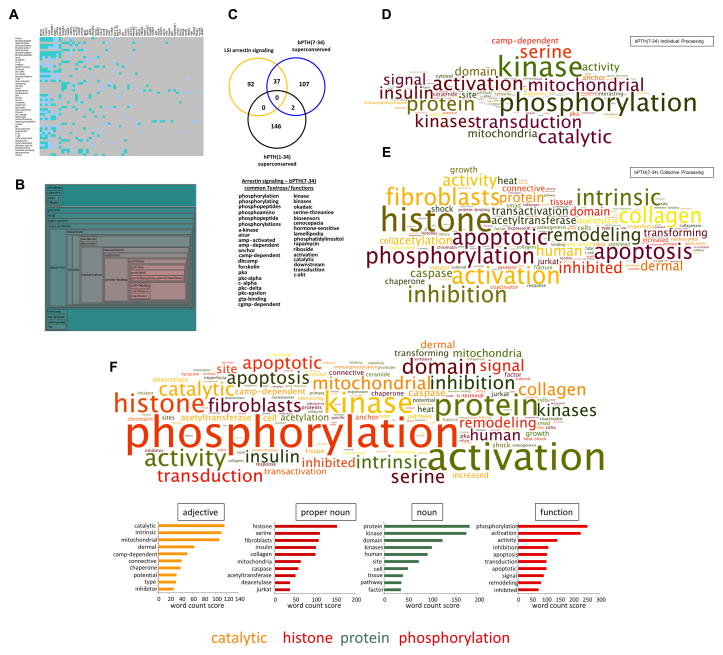
Fig. 6.
Defining in vivo arrestin-biased signaling using natural linguistic analysis: (A) Individual Textrous! processing of the superconserved multi-tissue transcriptomic dataset from bPTH(7-34)-treated animals. The heatmap blue-to-teal grid squares indicate a decreasing strength of statistical correlation between a specific gene and word: grey squares demonstrate a lack of correlation. (B) Collective Textrous! processing of the superconserved multi-tissue transcriptomic dataset from bPTH(7-34)-treated animals. The hierarchical wordcloud indicates the strength of correlation (size of text (larger = greater correlation) and green-to-red (red = high correlation) hue of the cloud). (C) The combined Textrous! analysis of the LSI-derived theoretical ‘arrestin signaling’ theoretical dataset (yellow circle) and the superconserved hPTH(1-34) (black circle) and bPTH(7-34) (blue circle) datasets was assessed for intersections using Venn analysis. The superconserved bPTH(7-34)-mediated transcriptomic responses demonstrate a considerably more arrestin-biased action compared to hPTH(1-34). The specific significantly-associated words, common between the output from the theoretical ‘arrestin signaling’ set and the empirical bPTH(7-34) transcriptomic superconserved set, are indicated in the lower panel. (D) Wordcloud interpretation of the individual Textrous! output (dismantled noun–phrases) from the bPTH(7-34) superconserved dataset. (E) Wordcloud interpretation of the collective Textrous! output (dismantled noun-phrases) from the bPTH(7-34) superconserved dataset. (F) Wordcloud interpretation of the collective + individual Textrous! outputs (dismantled noun–phrases) from the bPTH(7-34) superconserved dataset. Syntactic clustering of the highest word count elements in the lower panel (adjective, proper noun, noun, function) facilitates a coherent natural language-based specific interpretation of the high-dimensionality nature of the biased signaling effects of bPTH(7-34) at a systems-level.