Figure 2.
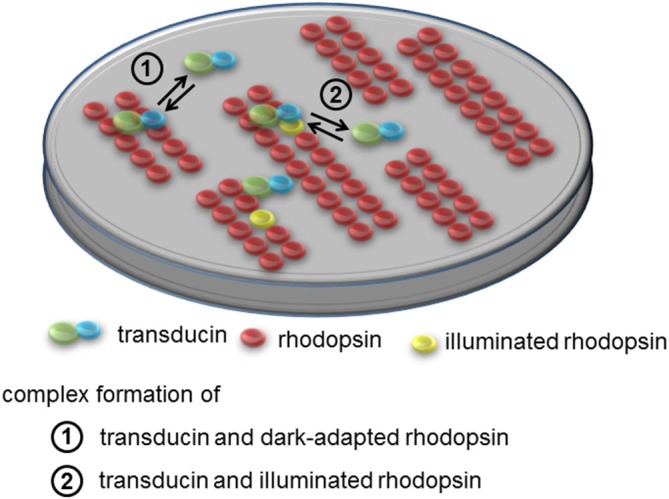
Supramolecular organization of rhodopsin and interaction with transducin. Rhodopsin is present in tracks of dimers in the disc membrane. In the dark rhodopsin-transducin complexes form with submicromolar affinity that is characterized by very fast association and dissociation rates. Movements of transducin can be described as dynamic hopping on rhodopsin supramolecular assemblies thus constituting “dynamic scaffolding”. Apparent dissociation rates of transducin from dark-adapted rhodopsin are >300-fold faster than corresponding rates from light-activated rhodopsin.
