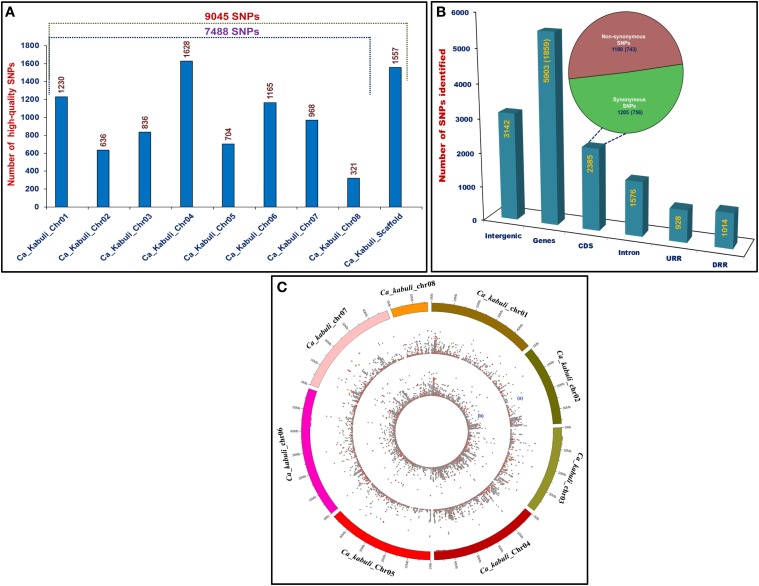
Figure 1.
(A) Frequency distribution of 9045 SNPs discovered employing reference kabuli genome (eight chromosomes and scaffolds)-based GBS and candidate gene-derived SNP genotyping assays. (B) Structural annotation of SNPs in the diverse coding (synonymous and non-synonymous) and non-coding (intron, URR, and DRR) sequence components of genes and intergenic regions of kabuli genome. The gene annotation information of kabuli genome (Varshney et al., 2013) was considered as reference to infer CDS (coding sequences)/exons, URR (upstream regulatory region) and DRR (downstream regulatory region) sequence components of genes. (C) A Circos circular ideogram depicting the relative distribution of 9045 SNPs, including non-synonymous SNPs (marked with red dots) physically mapped on eight kabuli chromosomes. The outermost circles illustrate the eight kabuli chromosomes coded with different colors, while the two inner circles “a” and “b” represent the distribution of SNPs mined from 93 cultivated (desi and kabuli) and 79 wild chickpea accessions, respectively.