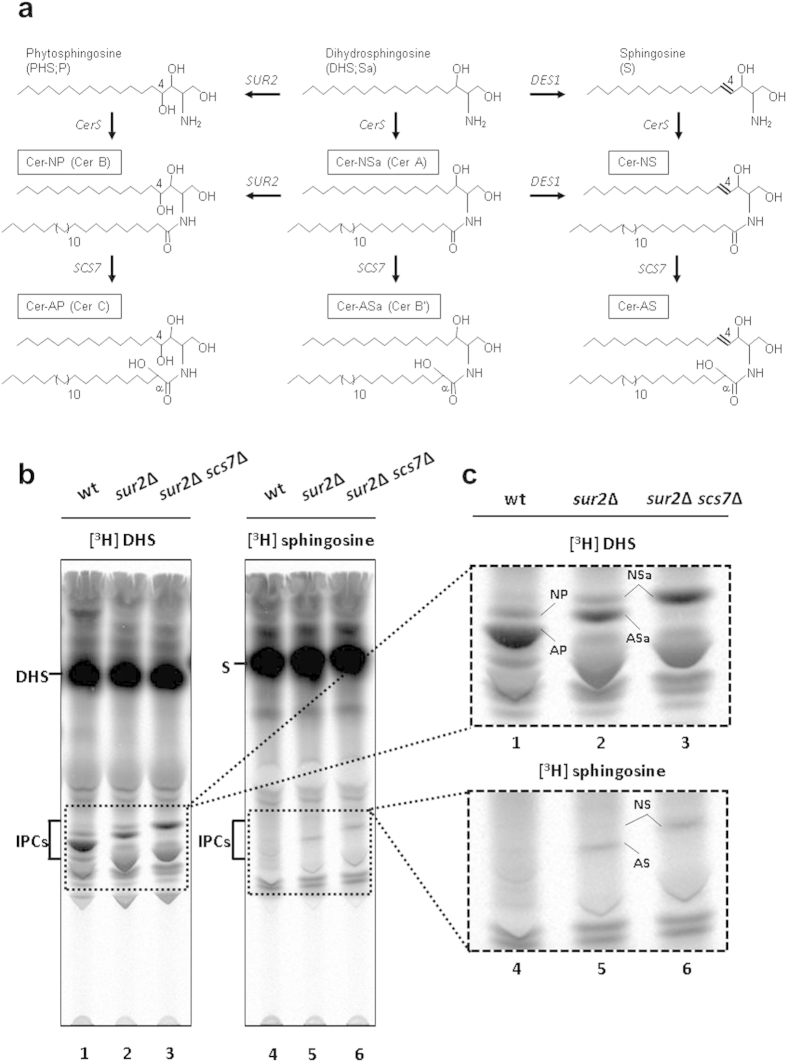
Figure 1. Sphingosine is metabolized to inositolphosphorylceramide in the Saccharomyces cerevisiae C4 hydroxylase-deficient sur2Δ mutant.
(a) Structure of ceramides. The nomenclature of Motta et al.51 is used; Cer-NSa/Cer-ASa, Cer-NP/Cer-AP, and Cer-NS/Cer-AS contain dihydrosphingosine (DHS, Sa), phytosphingosine (PHS, P), and sphingosine (S), respectively, linked to non-hydroxyl acyl group (N) or alpha-hydroxyl acyl group (A). The denotations in parentheses give the ceramide classification as used in Haak et al.22. CerS, ceramide synthases; SUR2, yeast sphingolipid C4-hydroxylase gene; SCS7, yeast fatty acid alpha-hydroxylase gene; DES1, sphingolipid Δ4-desaturase gene. Ceramides are converted to inositolphosphorylceramides (IPCs, IPC-NSa, IPC-ASa, IPC-NP, IPC-AP, IPC-NS, IPC-AS) by IPC synthase. (b) Cells were labeled with [3H]DHS or [3H]sphingosine 37 °C for 3h. The labeled lipids were extracted, subjected to mild alkaline hydrolysis and separated by TLC with solvent system I. (c) The indicated regions of the TLC image in (b) are displayed in an enlarged view.