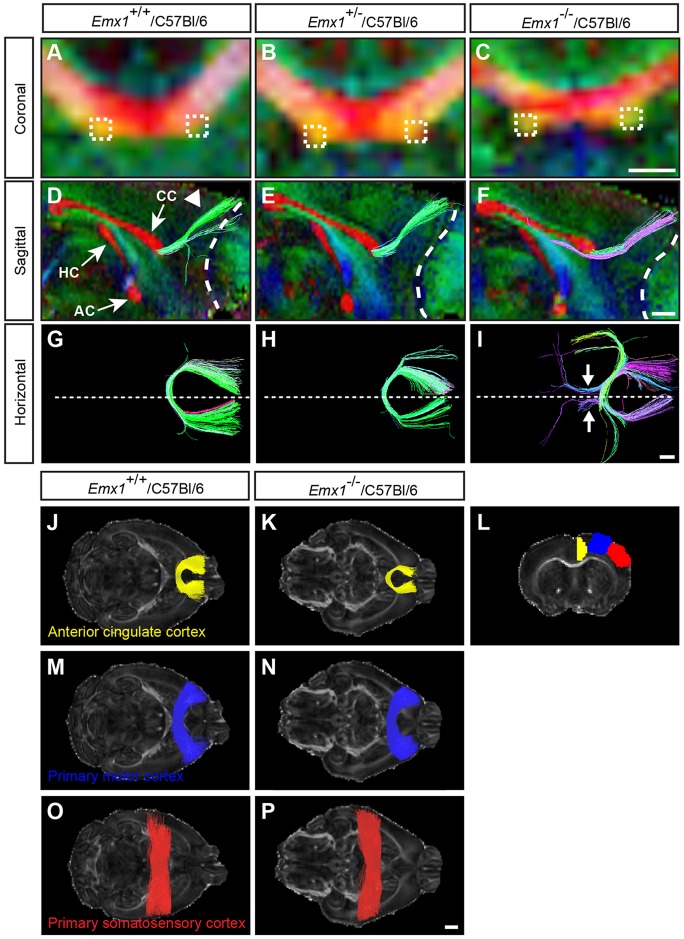
Fig. 2.
HARDI and tractography demonstrate that aberrant axonal bundles are associated with the anterior cingulate cortex. (A-C) Colored FA maps were generated in the coronal plane of the rostral corpus callosum using HARDI on adult Emx1/C57Bl/6 mice (n=5 per genotype). Dashed boxes placed on the aberrant axonal bundles (C) or at anatomically matched regions of the corpus callosum (A,B) represent the ROIs that were traced using Q-ball tractography. (D-F) Sagittal views of the forebrain at the midline (with rostral to the right) represented as colored FA maps with commissural projections shown in red (CC, corpus callosum; HC, hippocampal commissure; AC, anterior commissure), overlaid with tractography streamlines. (G-I) Horizontal view of tractography streamlines, oriented with rostral to the right. Tracts generated from the ROIs in A-C demonstrate streamlines projecting dorso-rostrally (arrowhead in D) into the anterior cingulate cortex in wild type (green streamlines in D,G) and heterozygotes (E,H) whereas in knockout animals the streamlines generated pass through the ROI and run rostro-caudally (purple streamlines in F,I, and arrows in I). Dashed lines in D-F outline the boundary between the olfactory bulb and the cortex, whereas dashed lines in G-I delineate the midline. For all colored FA maps, the predominant direction of white matter tracts is represented by these colors: red, medio-lateral; green, rostro-caudal; blue, dorso-ventral. (J-P) Streamlines were generated in the horizontal plane by seeding ROIs within the anterior cingulate (yellow streamlines), primary motor (blue streamlines), or primary somatosensory (red streamlines) cortex of one hemisphere, and restricting streamlines to those passing through the corpus callosum (n=5 per genotype). The coronal section in L demonstrates the seed ROIs from which streamlines were generated. Emx1−/−/C57Bl/6 mice demonstrate reduced homotopic connections that are specific to the anterior cingulate cortex and not the primary motor or somatosensory cortices. Scale bars: in C, 500 μm for A-C; in F, 2 µm for D-F; in I, 1 µm for G-I; in P, 1 mm for J-P.