Figure 2.
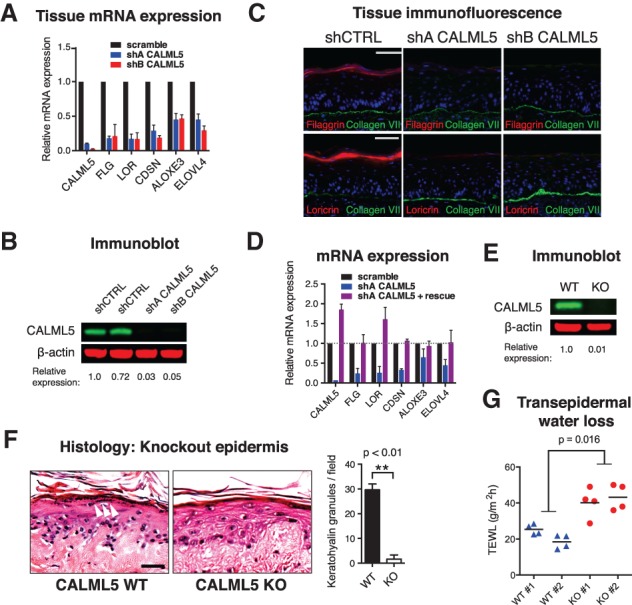
CALML5 is required for epidermal differentiation. (A) Quantitative RT–PCR (qRT–PCR) of mRNA from human organotypic epidermal tissue. n = 3. Error bars indicate SEM. (B) Immunoblot of CALML5-depleted cells. Quantitation is relative to scramble control. (C) Immunofluorescence of control (shCTRL) and CALML5-depleted (shA and shB) human organotypic epidermis. Bar, 50 µm. (D) qRT–PCR of in vitro differentiated keratinocytes after CALML5 rescue. The dotted line indicates expression of control. n = 2. Error bars indicate SEM. (E) Immunoblot of CALML5 knockout cells generated by CRISPR/Cas9 editing of clone 103 human keratinocytes. Scrambled guide RNA was used to produce wild-type control. (F) Hematoxylin and eosin stain of CALML5 wild-type and knockout xenografted human epidermal tissue. White arrowheads indicate keratohyalin granules. Bar, 50 µm. Quantitation of keratohyalin granules is shown at right. (G) Transepidermal water loss of CALML5 wild-type and knockout xenografts on live mice. n = 2 per condition. Four measurements were performed per graft; horizontal lines denote the average.
