Figure 4.
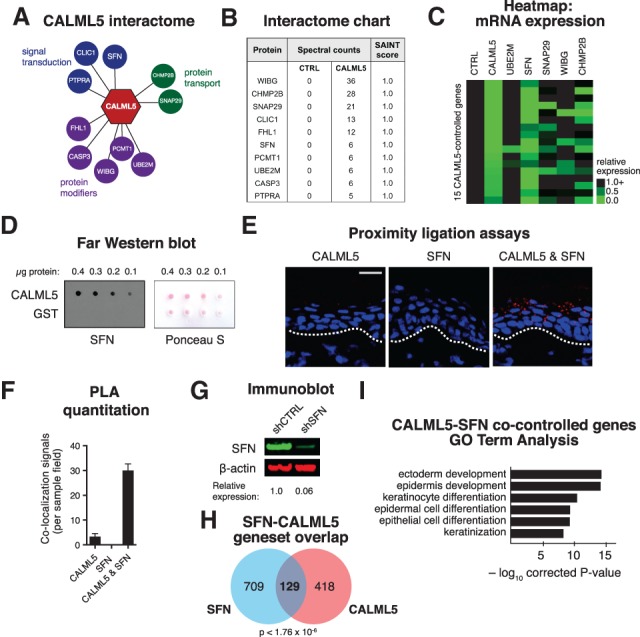
CALML5 interacts with SFN to promote epidermal differentiation. (A) The CALML5 protein interactome as defined by proximity-dependent BioID/MS. (B) Table of spectral counts and SAINT scores of interacting proteins. (C) Heat map of 15 CALML5 target gene expression levels (rows), as measured by qRT–PCR, after RNAi depletion of candidate interacting genes (columns). (D) Far Western blot with recombinant CALML5 or glutathione S-transferase (GST) control, probed with recombinant SFN protein. At right, Ponceau S loading control. (E) Proximity ligation assays (PLAs) in human epidermis with antibodies to CALML5, SFN, or both. Bar, 50 µm. (F) Quantitation of PLA colocalization. (G) Immunoblot of control and SFN-depleted keratinocytes. Quantitation is relative to scramble control. (H) Venn diagram showing overlap of SFN- and CALML5-controlled gene sets. (I) GO analysis of the CALML5–SFN overlap gene set.
