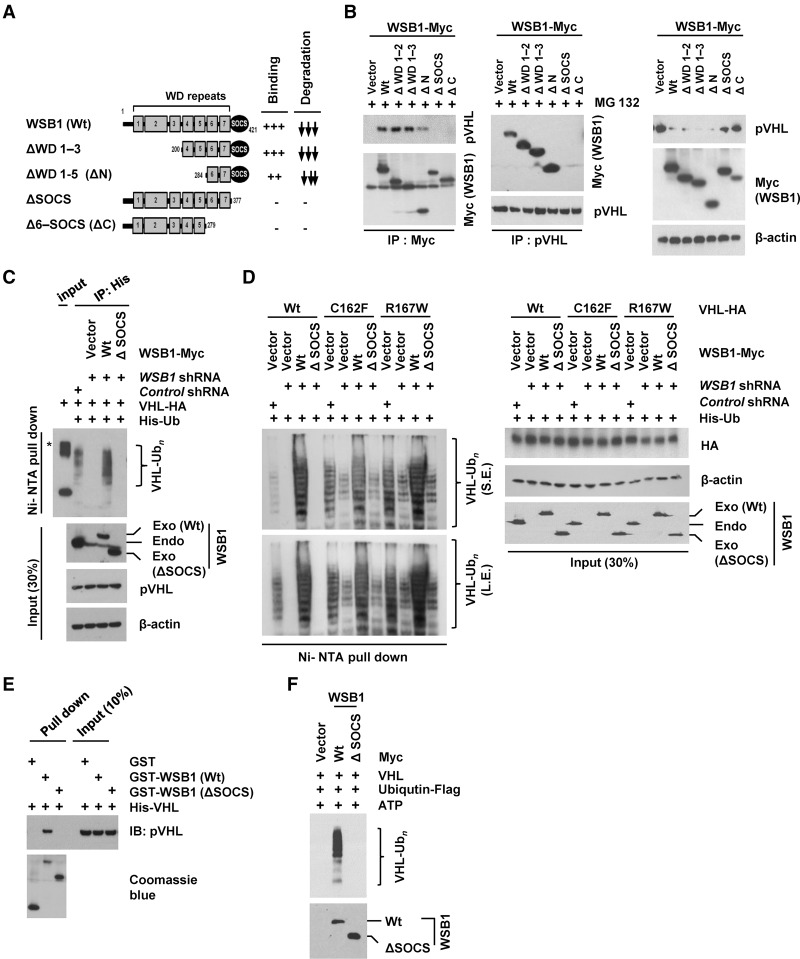
Figure 3.
WSB1 interacts with pVHL and promotes pVHL ubiquitination through the its SOCS domain. (A) Diagrams of wild-type WSB1 and corresponding deletion mutants (ΔWD 1–3, ΔWD 1–5, ΔSOCS, and Δ6-SOCS) used in co-IP experiments with pVHL. Plus and minus symbols indicate the binding affinity of each WSB1 mutants with the pVHL, and arrows indicate the effect of the WSB1 mutants (decreasing pVHL stability). (B) Cells were transfected with the indicated plasmids. (Left) Cells were pretreated with MG132, and the WSB1–pVHL interaction was examined by immunoprecipitation. (Right) pVHL levels were examined without MG132 pretreatment. (C) Deletion of WSB1's SOCS domain inhibits WSB1's E3 ligase activity toward pVHL. Cells were transfected with the indicated constructs and then treated with MG132. Ubiquitinated proteins were pulled down under denaturing conditions by Ni-NTA agarose and analyzed by immunoblot. An asterisk indicates a nonspecific band. (Exo) Exogenous; (Endo) endogenous. (D) HEK293T cells were transfected with the indicated constructs, including wild-type pVHL or loss of E3 ligase function pVHL (C162F and R167W). Cells were then treated with MG132. Ubiquitinated proteins were pulled down under denaturing conditions by Ni-NTA agarose and analyzed by immunoblot. WSB1 antibody was used to detect both endo-WSB1 and exo-WSB1 levels. (S.E.) Short exposed; (L.E.) long exposed; (Exo) exogenous; (Endo) endogenous. (E) In vitro binding assay of recombinant WSB1 with pVHL was performed. (F) WSB1 (wild-type or ΔSOCS) was purified from cells and used in an in vitro ubiquitination reaction using recombinant pVHL.