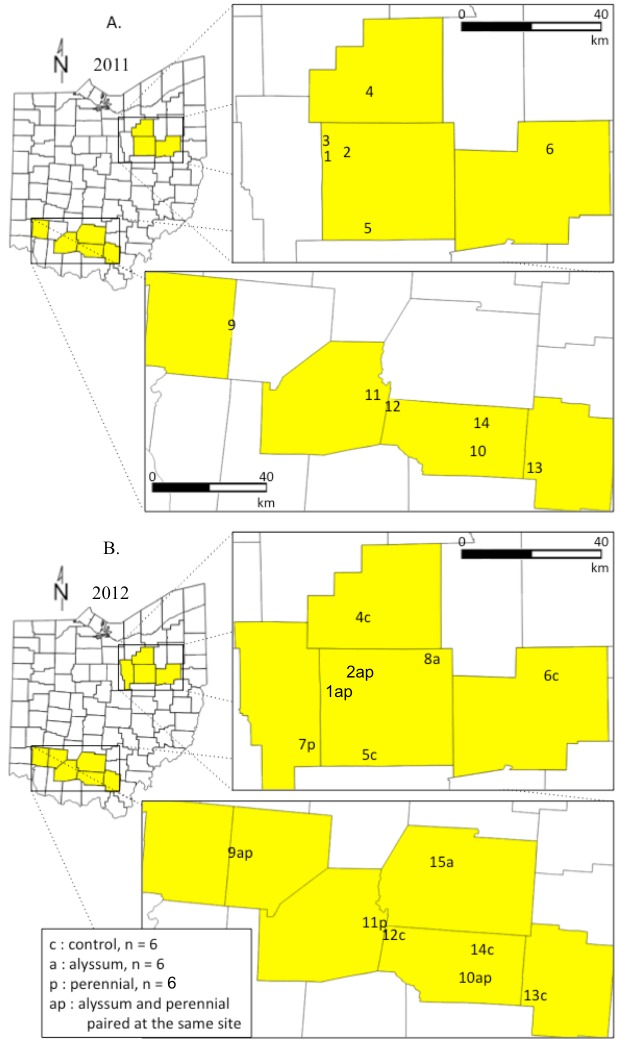
Figure 1. Pumpkin sites were located in growing regions in northern and southern Ohio.
In 2011, we established 12 pumpkins sites on individual farms. We did not evaluate habitat management in 2011; each pumpkin site was adjacent to a grassy field border. In 2012, we added 6 additional pumpkin sites for a total of 18. Each site was assigned to one of three habitat management treatments: GRASS CONTROL (pumpkin plot adjacent to a 6 × 60 m grass area, mowed approximately once per month) (2) ALYSSUM (pumpkin plot planted between two 60 m rows of the non-native annual, L. maritima), and (3) PERENNIAL (pumpkin plot planted adjacent to a 6 × 60 m buffer of native perennial wildflowers). These sites were located on 15 farms. Each farm had one pumpkin site except for farms 1, 2, 9, and 10 where both one ALYSSUM and one PERENNIAL treatment site were established. The distances between these plots ranged from 51 m at site 10, to 570 m at site 9.