Fig. 6.
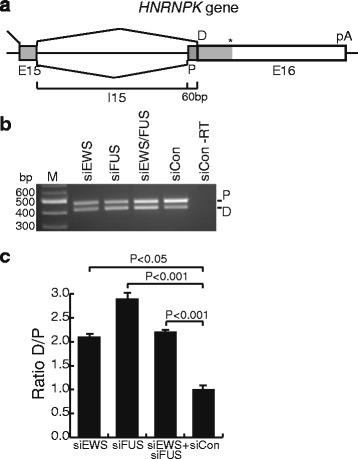
FUS and EWS influence HNRNPK splice site selection. a Graphical illustration of HNRNPK alternative splice acceptor site selection in exon 16. P, proximal splice site; D, distal splice site. On top are indicated the coding region in gray and positions of translational stop (*) and Poly(A)-signal (pA). b RT-PCR and gel electrophoresis of siEWS, siFUS, siEWS and siFUS, and siControl depleted HEK-293 cells. This image is representative of 3 independent experiments. M, 100 bp DNA ladder. –RT, negative control of PCR mix without template cDNA. c Ratio of D (distal) to P (proximal) splice acceptor site usage in siRNA transfected cells. The ratio was calculated from relative band intensity values by GelQuant software. The ratio for siCon was given the value 1 and the ratios from siRNA-depleted samples were calculated accordingly. Experiments were performed in biological triplicates. Data presented as mean + SEM
