Scheme 1.
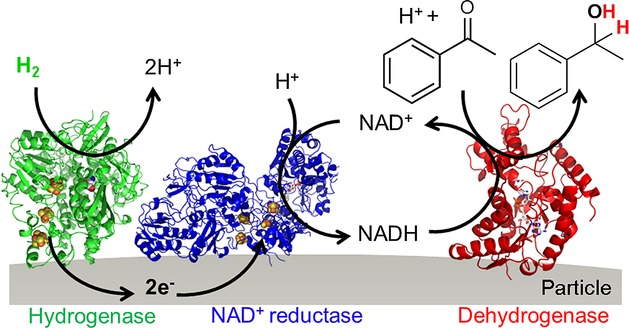
Schematic representation of the H2-driven particle system for NADH-dependent biocatalysis. Oxidation of H2 by a hydrogenase (green) transfers electrons (e−) into an electronically conducting particle and these are then used by an NAD+ reductase (blue) for selective NAD+ reduction. A co-immobilised NADH-dependent AHD (red) is supplied with NADH that is used for catalytic reduction of a ketone (here, acetophenone). Both hydrogen atoms of H2 are incorporated into the product (here phenylethanol) to allow a 100 % atom-efficient chemical synthesis.
