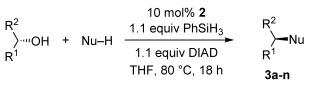
Table 2.
The substrate scope of the catalytic Mitsunobu reaction[a]
| Entry | Product | Catalytic yield [%][b] | Stoichiometric yield [%][b,c] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 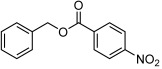 |
3 a | 77 | 94 |
| 2 | 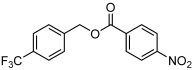 |
3 b | 76 | 92 |
| 3 | 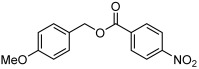 |
3 c | 61 | 80 |
| 4 | 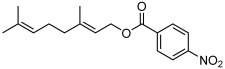 |
3 d | 50 | 50 |
| 5 | 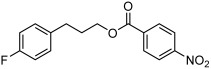 |
3 e | 82 | 82 |
| 6 | 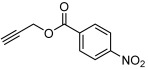 |
3 f | 84 | 90 |
| 7 | 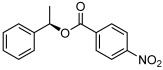 |
3 g | 69[d] | 77[d] |
| 8 |  |
3 h | 68[e] | 78[e] |
| 9 | 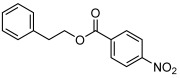 |
3 i | 76 | 96 |
| 10 |  |
3 j | 63 | 83 |
| 11 | 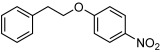 |
3 k | 51[f] | 85[f] |
| 12 | 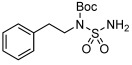 |
3 l | 72 | 90 |
| 13 | 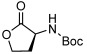 |
3 m | 87[g,h] | 98[g] |
| 14 |  |
3 n | 70[i] | 93[i] |
[a] Reactions performed on 0.5–1.0 mmol scale at 0.25 m employing 1.5 equiv of pronucleophile, 10 mol % loading of catalyst 2, and 1.1 equivalents of both DIAD and PhSiH3. Reactions were all run at 80 °C. [b] Isolated average of two reactions. [c] Reactions performed at 23 °C with 1.5 equivalents of pronucleophile, TPP, and DIAD without phenylsilane for 18 h. [d] e.r. 94:6. [e] e.r.>99.5:0.5. [f] 48 h. [g] Concentration was 0.04 m. [h] Background reaction with only Boc-homoserine-OH, DIAD, and PhSiH3 only produced traces. [i] N-Boc sulfamide (3 equiv) was used as the pronucleophile.
