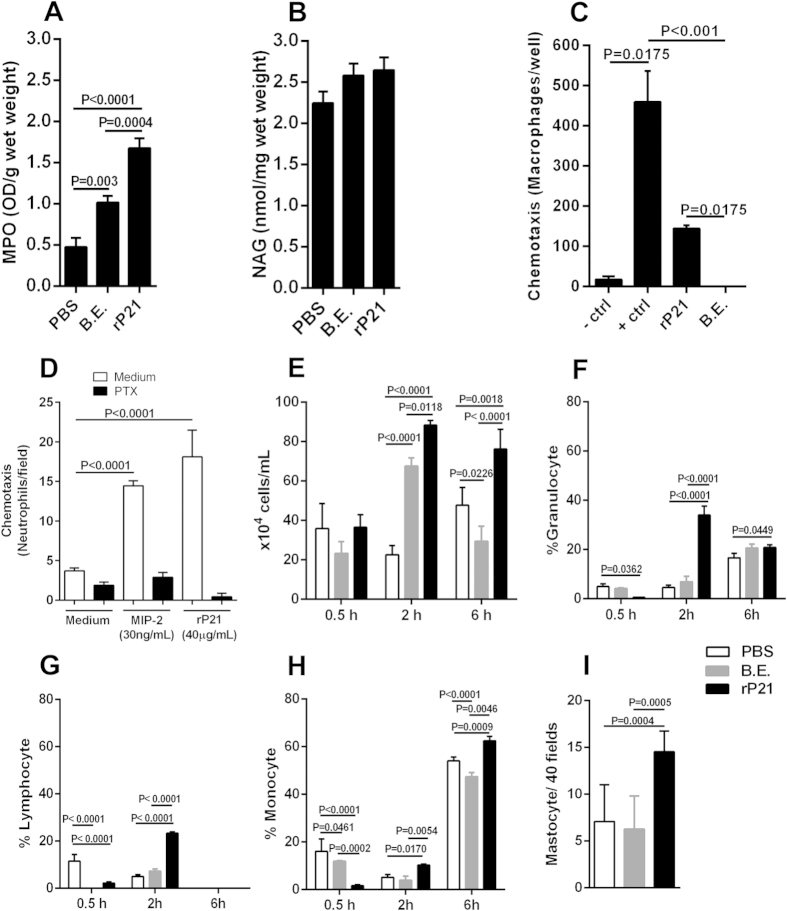
Figure 2. rP21 promoted myeloperoxidase expression and leukocytes chemotaxis.
rP21 treatment enhanced the levels of myeloperoxidase (MPO) (A) but not of N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminidase (NAG) (B). rP21 but not B.E. induced macrophage migration in a trans-well system. Negative control (-control): serum-free medium; Positive control (+control): stromal cell-derived factor 1 (SDF-1α – CXCL12) (C). rP21 promoted neutrophil chemotaxis in Boyden chamber. This activity was completely abolished by previous cell treatment with pertussis toxin (PTX; negative control). Positive control: macrophage inflammatory protein (MIP-2) Experiments were performed four times in triplicate (D). rP21 treatment induced the recruitment of higher number of total leukocytes to mice peritoneal cavity (E). Phenotypic cell identification showed that at two hours rP21 promoted higher recruitment of granulocytes (F), lymphocytes (G) and monocytes (H). The ability of rP21 to recruit higher number of monocytes extended up to six hours post-inoculation. Higher number of mastocytes was observed in rP21-treated sponges compared to PBS and B.E. treatments. Experiments were performed twice using 6 animals/group. Samples were analyzed individually (I). 40 μg/mL of rP21 and B.E. were used. Data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation of experiments performed in triplicate. Significant differences were determined by one-way (A,B,C,D,I) or two-way ANOVA (E,F,G,H) and Turkey’s multiple comparisons test (GraphPad Prism software, version 6.01). Differences were considered significant when p < 0.05.