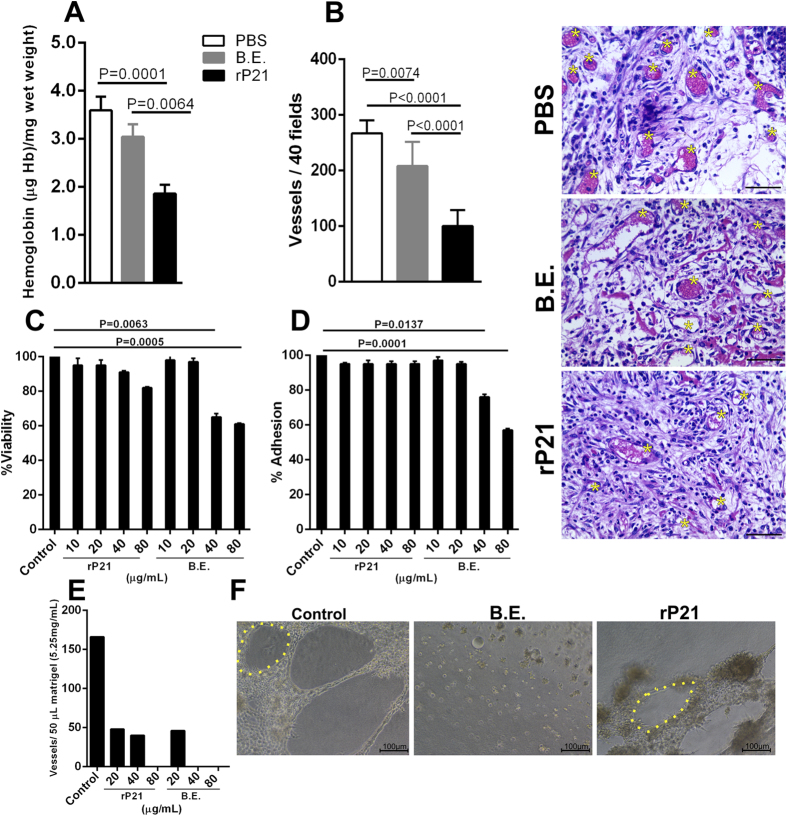
Figure 3. rP21 inhibited angiogenesis in vivo and in vitro.
Decrease in hemoglobin content was observed in rP21 treated sponges (A). Sponges treated with rP21 showed a decreased number of blood vessels compared to the control treatments (B). Representative HE-stained sponges are shown (panel on the up-right position) and yellow asterisks indicate blood vessels. 40 μg/mL of rP21 and B.E. were used. rP21 did not alter tEnd cell viability (C), adhesion (D) to extracellular matrix and inhibited vessel formation (E). B.E. showed cell toxicity and inhibition of adhesion at the concentrations of 40 and 80 μg/mL (representative results of four independent experiments performed in triplicate). Representative images highlighting vessels morphology (yellow dotted line) are also shown (F). Data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation of experiments performed in triplicate. Significant differences were determined by one-way ANOVA and Turkey’s multiple comparisons test (GraphPad Prism software, version 6.01). Differences were considered significant when p < 0.05.