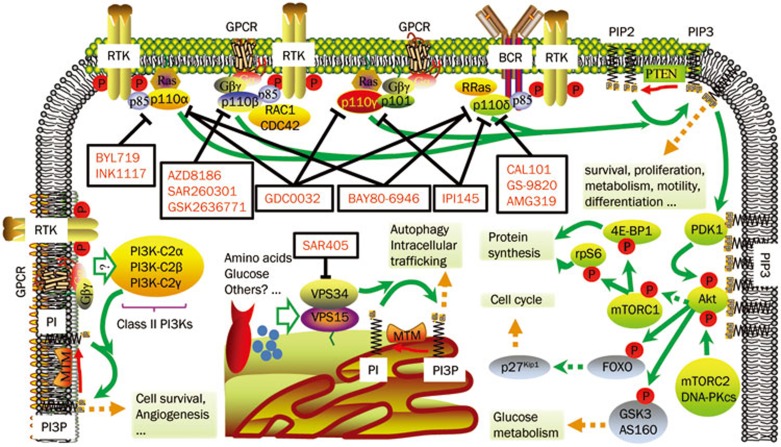
Figure 1.
Divergent regulation of PI3K isoforms and isoform-selective inhibitors. PI3Kα is activated by RTKs and Ras; PI3Kβ is the downstream kinase of RTKs, GPCRs and RAC1/CDC42; PI3Kγ mediates signals from GPCRs and Ras, while PI3Kδ is under the control of RTKs and antigen receptors. Class I PI3Ks produce the second messenger PIP3, which promotes cell survival, proliferation, metabolism, motility and differentiation. One of the key mediators is Akt, which is phosphorylated and activated by PDK1 and mTORC2 or DNA-PKcs in the presence of PIP3. Akt further phosphorylates diversified substrates and regulates protein synthesis, cell cycle and glucose metabolism. PTEN acts as a negative regulator and removes the 3′ phosphate from PIP3. The potential inputs of class II PI3Ks include GPCRs and RTKs, and their product PtdIns(3)P (PI3P) has a role in cell survival and angiogenesis. Amino acids, glucose and certain GPCRs are reported as stimuli of Vps34, which is able to produce PI3P to regulate autophagy and intracellular trafficking. The MTM phosphatase family removes 3′ phosphate from PI3P and terminates its signaling. Representative inhibitors of each isoforms are highlighted in red and are listed in Table 1.