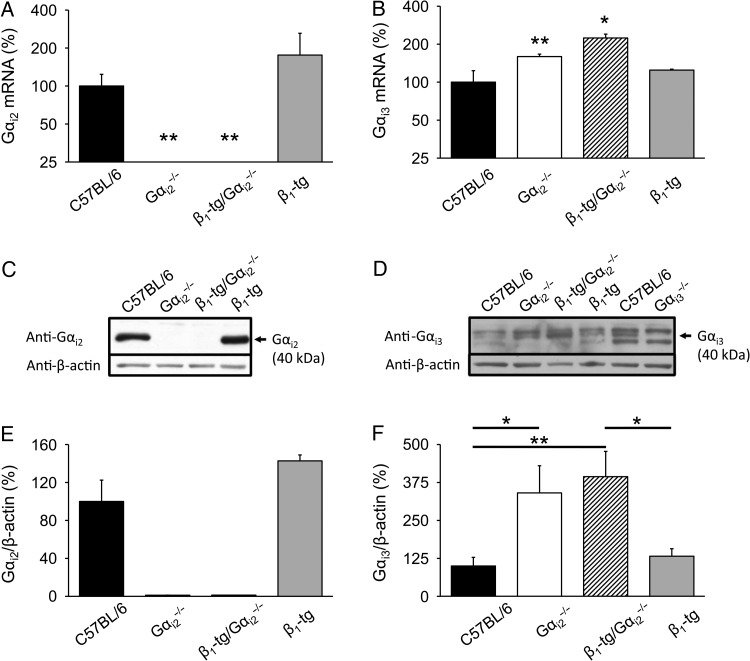
Figure 5.
Ventricular expression of cardiac Gi. (A) Gαi2 mRNA was not detectable in knockout mice on either wild-type or β1-transgenic background and expressed at wild-type level in mice only transgenic for the β1-adrenoceptor. (B) Gαi3 mRNA expression was significantly increased compared with wild-type mice in animals lacking Gαi2 on both a wild-type and β1-transgenic background, respectively. The number of animals used for qPCR analysis was 3–4 for each genotype. Age range of examined mice was 302 ± 4 days. Asterisks indicate significant differences compared with mRNA expression levels of age-matched wild-type mice in an REST® analysis (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01). (C) Representative immunoblots for the Gαi2 protein in ventricle homogenates. The Gαi2 protein was absent in Gαi2−/− and β1-tg/Gαi2−/− mice. (E) Statistical analysis of Gαi2 expression levels. (D) Representative immunoblot for the Gαi3 protein in ventricle homogenates. To verify Gαi3 antibody specificity, Gαi3-deficient ventricle homogenates were loaded in addition. (F) Statistical analysis of Gαi3 expression levels. A significant up-regulation of Gαi3 protein levels was detectable in Gαi2−/− and β1-tg/Gαi2−/− mice. For western blots, individual homogenates from three animals per genotype were analysed in 3–4 independent experiments. β-Actin was used to demonstrate equal loading of the gels. Asterisks indicate significant differences in Bonferroni post-tests following ANOVA (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01).