Figure 11.
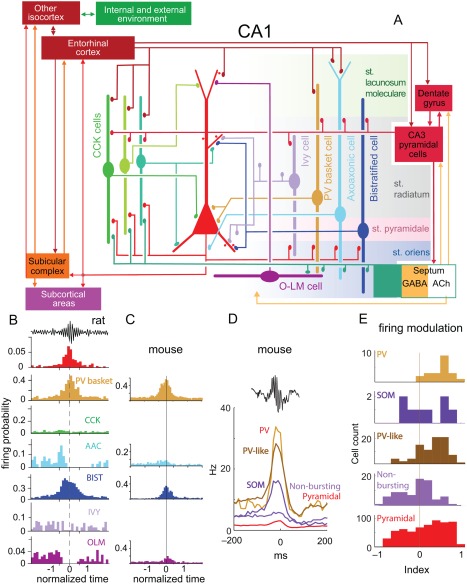
SPW‐R‐related firing patterns of interneurons. (A) Schematic of the main synaptic connections of pyramidal cells (red, middle), three types of CCK‐expressing cells (basket cell, perforant path‐associated cell, Schaffer collateral‐associated cell), ivy cells and PV‐expressing basket, axo‐axonic, bistratified and O‐LM interneurons. Connections among interneurons are not shown. (B) Firing probability histograms; averages from several cells of the same type recorded in anaesthetized rats. Note different scales for the y‐axis. (C) Firing probability histograms for non‐anesthetized mice. In B and C all neurons were labeled juxtacellularly and identified histologically. (D) Firing patterns of optogenetically identified PV‐expressing and SOM‐expressing interneurons during SPW‐Rs. Also shown are putative, physiologically characterized interneurons. Note that almost all PV and PV‐like neurons were robustly active during ripples, whereas the firing behavior of SOM, non‐bursting and pyramidal cells was variable. (E) Distribution of ripple modulation index in the five cell groups. The bimodal behavior of SOM neurons may represent a mixture of O‐LM (ripple‐activated) and bistratified (ripple suppressed) interneurons. Modulation index: the mean firing rate between −150 and −50 ms is subtracted from the mean rate between −50 and 50 ms and normalized. Positive (negative) indexes indicate an increase (suppression) of firing during SPW‐Rs. A and B, reproduced from Somogyi et al., (2014). C, Reproduced from Varga et al. (2012). D, E, reproduced from Royer et al. (2012).
