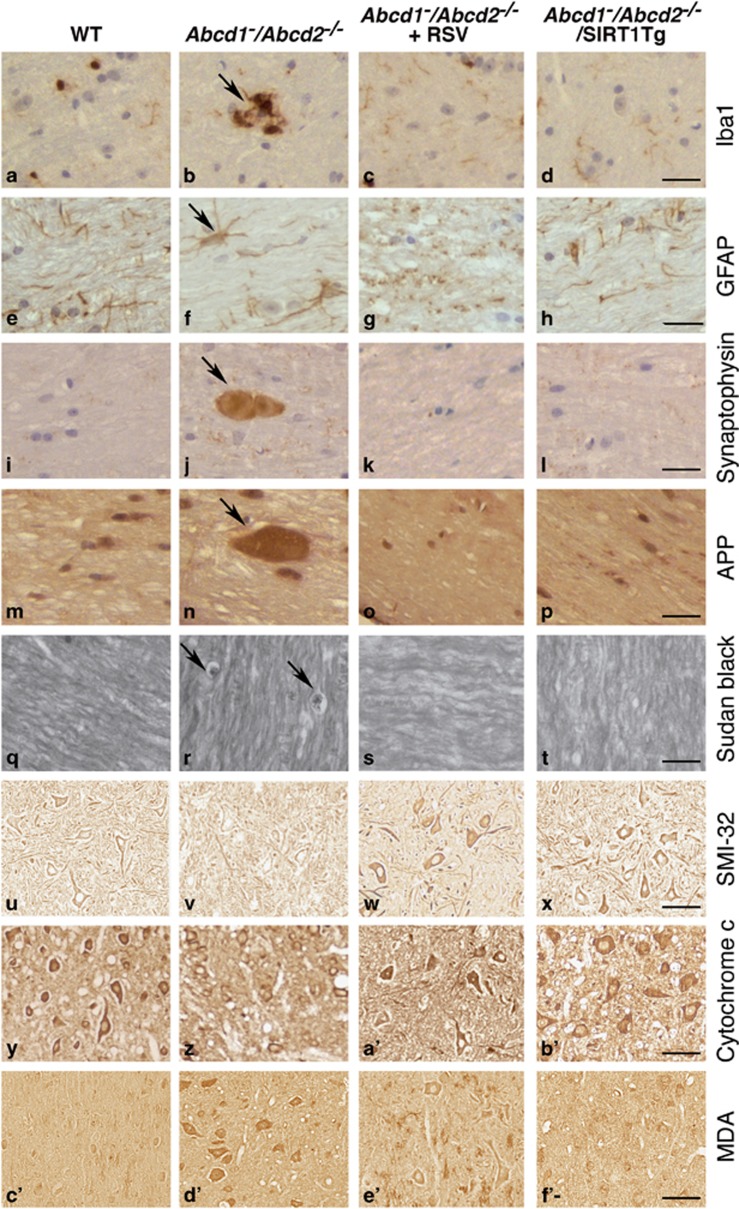
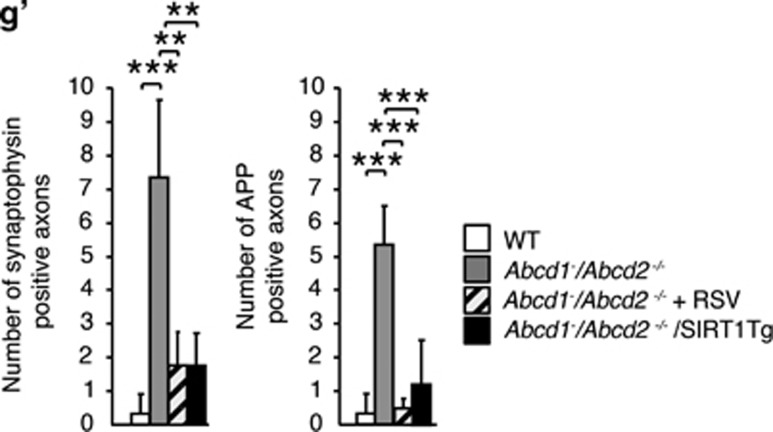
Figure 6.
Activation of SIRT1 normalizes axonal degeneration in Abcd1−/Abcd2−/− mice. (a–f') Immunohistological analysis of axonal pathologies performed in 18-month-old WT, Abcd1−/Abcd2−/− and Abcd1−/Abcd2−/− mice treated with RSV (Abcd1−/Abcd2−/−+RSV) and in WT, Abcd1−/Abcd2−/− and Abcd1−/Abcd2−/− mice with transgenic overexpression of SIRT1 (Abcd1−/Abcd2−/−/SIRT1Tg) (n=5 per genotype and condition). Spinal cord immunohistological sections were processed for (a–d) Iba1, (e–h) GFAP, (i–l) synaptophysin, (m–p) APP, (q–t) Sudan black, (u–x) SMI-32, (y–b') Cytochrome c and (c'–f') MDA. Representative images for (a, e, i, m, q, u, y and c') WT, (b, f, j, n, r, v, z and d') for Abcd1−/Abcd2−/−, (c, g, k, o, s, w, a' and e') for Abcd1−/Abcd2−/−+RSV and (d, h, l, p, t, x, b' and f') for Abcd1−/Abcd2−/−/SIRT1Tg mice are shown. Scale bar=25 μm. (g') Quantification of synaptophysin and APP accumulation in spinal cord immunohistological sections of WT, Abcd1−/Abcd2−/−, Abcd1−/Abcd2−/−+RSV and Abcd1−/Abcd2−/−/SIRT1Tg mice. Values are expressed as mean±S.D. (*P<0.05, **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001, one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's HSD post hoc)