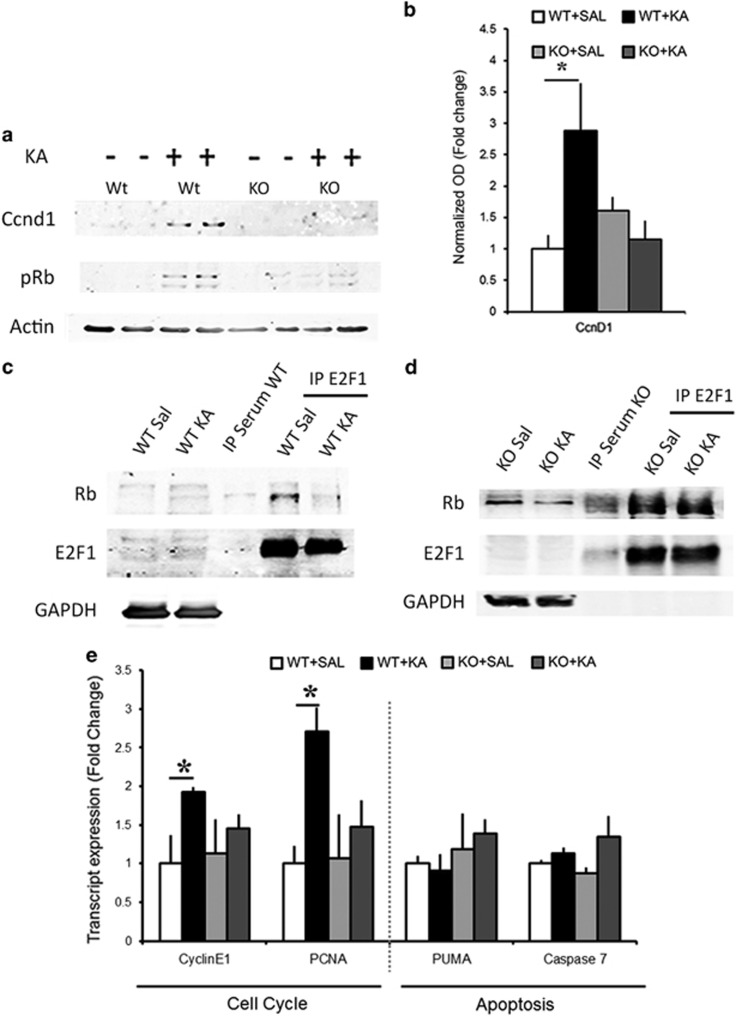
Figure 4.
KA treatment induces Ccnd1/E2F1 activation and is Notch signaling dependent. (a) Representative immunoblots of hippocampal CA lysates show the changes in Ccnd1 expression and Rb phosphorylation in WT and RBPJKcKO hippocampi upon KA as compared with Saline controls. (b) Graph summarizing the fold changes in the optical density of Ccnd1 in WT and KO hippocampi (n=6 per condition and genotype). (c) Representative immunoblot shows that the E2F1:Rb interaction is reduced upon KA as compared with Saline in the WT mice. No trace of protein is visible in the control IP sample with serum. GAPDH is used to control for loading of the inputs and contamination in the IP samples (n=3 independent IPs). (d) Representative immunoblot shows that Rb:E2F1 interaction is prominent even after KA treatment in the RBPJKcKO mice as compared with Saline. The GAPDH band serves as in C (n=3 independent IPs). (e) Graph summarizing transcript expression of E2F1 targets in WTs and RBPJKcKOs upon KA as compared with Saline (n=3–6 per condition). Asterisks indicate significant differences. Error bars represent mean±S.E.M.