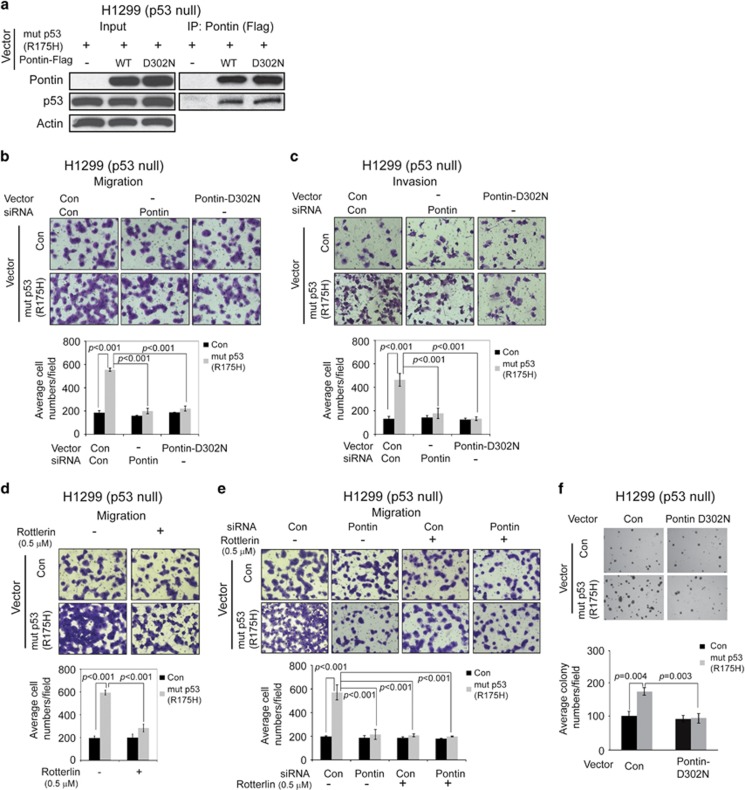
Figure 4.
The ATPase activity in Walker B motif is required for Pontin to promote mutp53 GOF in migration, invasion and anchorage-independent cell growth. (a) The ATPase-deficient dominant-negative mutant Pontin-D302N bound to mutp53 protein. H1299 cells were co-transfected with expression vectors of mutp53 (R175H) along with wild-type Pontin or Pontin-D302N for co-IP assays. (b and c) Ectopic expression of Pontin-D302N largely blocked mutp53 GOF in migration (b) and invasion (c) as determined by transwell assays. H1299-Con and H1299-R175H cells were transfected with expression vectors of Pontin-D302N or control vectors. Cells were also transfected with siRNA against Pontin or control siRNA to compare the effect of Pontin-D302N with knockdown of endogenous Pontin on mutp53 GOF in migration and invasion. (d) Rottlerin, a Pontin-specific small molecular ATPase inhibitor, greatly compromised mutp53 GOF in migration. H1299-Con and H1299-R175H cells were treated with Rottlerin (0.5 μM) for 48 h, and their migration abilities were determined by transwell assays. (e) Combined treatments of Rottlerin and Pontin knockdown did not have an additive or synergistic effect on downregulation of mutp53 GOF. H1299-Con and H1299-R175H cells were subjected to following treatments: transfection with siRNA against Pontin, treatment with Rottlerin or Pontin knockdown by siRNA followed by Rottlerin treatment as indicated. The migration abilities of cells were determined by transwell assays. (f) Ectopic expression of Pontin-D302N inhibited anchorage-independent cell growth on soft agar of H1299-R175H cells but not H1299-Con cells. H1299-R175H and H1299-Con cells were transfected with control or Pontin-D302N expression vectors. For (b–f), data are presented as mean±S.D. (n=3)