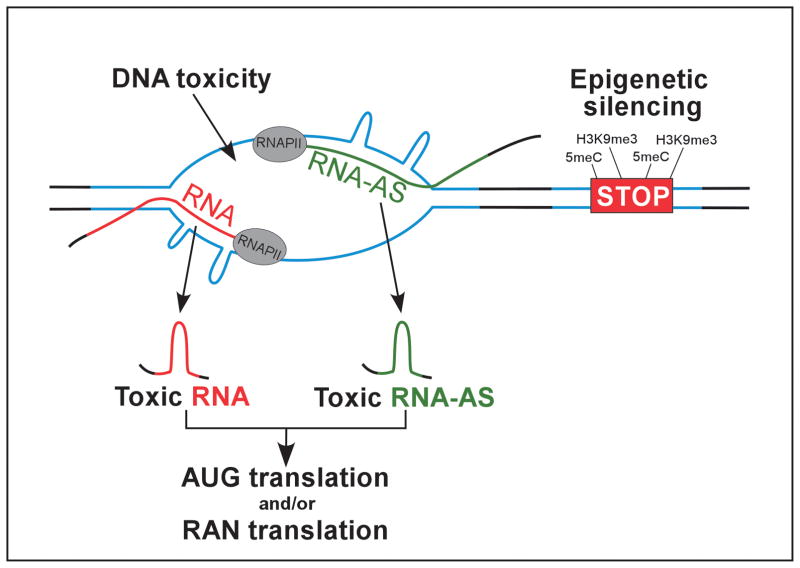
Figure 3. Molecular mechanisms of pathogenesis induced by expanded repeats.
Pathological consequences elicited by long repeat sequences can be classified into two categories (i) loss of gene expression due to the changes in the epigenetic landscape and (ii) consequences of RNA and/or protein expression, which includes RNA-toxic-gain of function induced by sense and/or antisense transcripts, as well as protein gain of function encompassing AUG-translated and RAN-translated proteins. DNA toxicity resulting from convergent transcription through the repeats may also contribute to the pathogenesis of URDs.