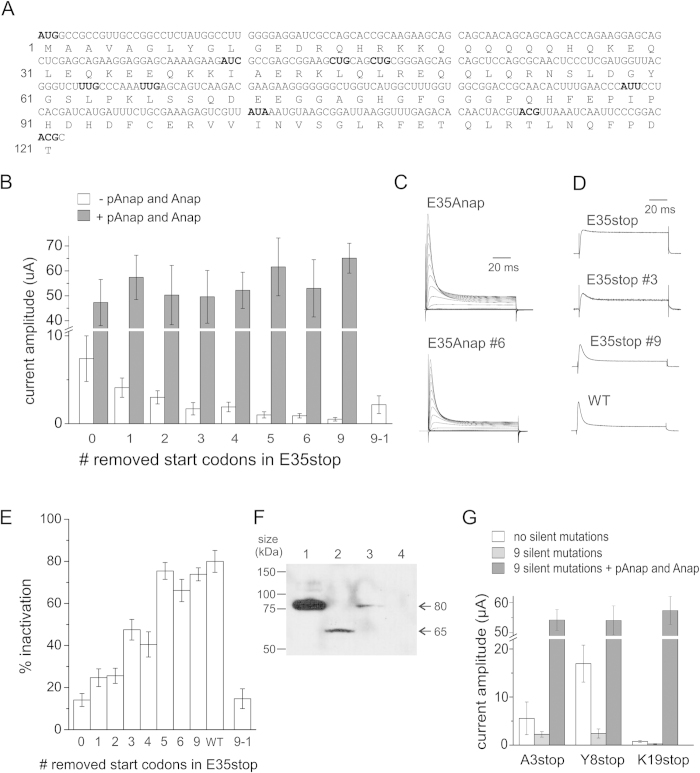
Figure 3.
A) Sequence of amino acids 1−121 and the corresponding mRNA nucleotides in Shaker. The nucleotides of the canonical start codon (M1) and the following 9 downstream non-canonical start codons (I40, L45, L47, I89, L36, L66, I101, T114, and T121) are shown in bold. AAG and AGG codons were ignored. Numbers refer to the amino acid sequence. B) Comparison of peak current amplitudes at +60 mV of E35stop with silent mutations, without and with Anap incorporation. Numbers refer to the number of mutated start codons such that 1 is E35stop-L45L, 2 is E35stop-L45L-L47L, 3 is E35stop-I40L-L45L-L47L, 4 is E35stop-I40L-L45L-L47L-L63L, 5 is E35stop-I40L-L45L-L47L-L63L-L66L, 6 is E35stop-I40L-L45L-L47L-L63L-L66L-I89L and 9 is E35stop-I40L-L45L-L47L-L63L-L66L-I89L-I101L-T114T-T121T. Error bars indicate SEM with n = 20–30 oocytes. C) Inactivation is recovered with Anap incorporation. Shown are examples of ionic currents from E35Anap and E35Anap #6 (six mutated start codons). Voltage protocols are the same as in Fig. 1. D) Comparison of inactivation measured as the ratio between the current amplitude at the end of the +60 mV pulse, and the maximum current amplitude. Error bars indicate SEM with n = 10–20 oocytes. E) Depolarization from −90 mV to +60 mV is shown for E35stop mutants and WT showing how inactivation increases when channel expression decreases. F) Western blot of isolated Xenopus oocytes membranes expressing Shaker WT (lane 1, 30 oocytes), E35stop (lane 2, 70 oocytes), E35Anap (lane 3, 30 oocytes) and non injected (lane 4, 70 oocytes). G) Comparison of peak current amplitudes at +60 mV for A3stop, Y8stop and K19stop, and removal of 9 start codons without and with Anap incorporation. Error bars indicate SEM with n = 5–10 oocytes.