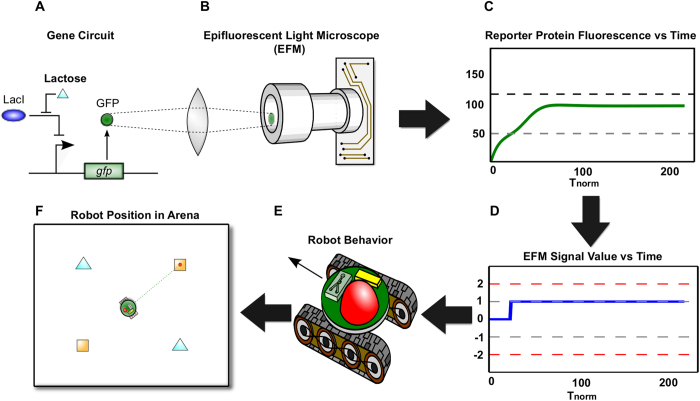
Figure 2. Computational Simulation Approach for the Model System.
(A) A basic gene circuit – the lac-inducible gene network – forms the core of all simulated gene network behavior. (B) Green fluorescent protein (GFP, shown as a green dot) from this circuit is conceptualized to be detected by an onboard miniature, epifluorescent microscope (EFM). (C) A computational simulation of microbiome GFP production based upon an analytical model for the circuit in (A). In a built-system, this protein fluorescence signal would be the light detected by the EFM. (D) The conceptualized robot uses onboard electronics to convert the measured light signals into electrical (voltage) signals. (E) Voltage signals meeting specific criteria activate pre-programmed robot motion subroutines. (F) The resulting emergent behavior potentially leads a robot to a carbon fuel depot. Here, robot behavior resulting from a simulation of the circuit in (A) is shown. The robot was programmed with motion subroutines that activate to seek arabinose (orange square) depots following receipt of lactose (cyan triangles).