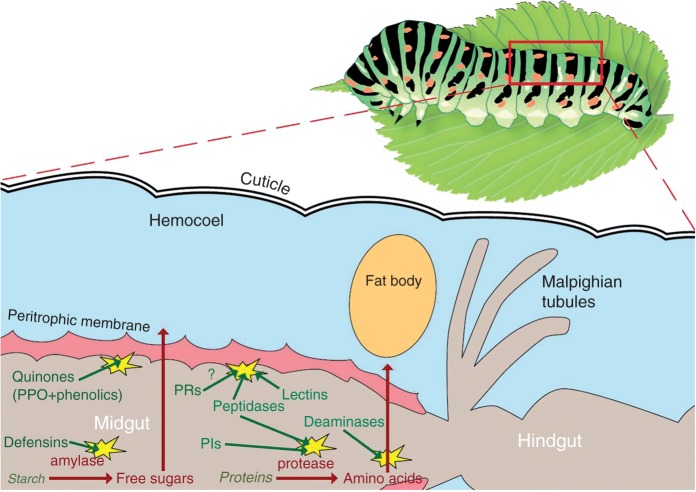
Fig. 3.
Mode of action of plant defence proteins in the herbivore gut. Herbivores utilize plant material predominantly to obtain sugar and amino acids. They digest proteins into amino acids via proteases and starch/sucrose into free sugars via amylases/invertases. Plants produce special proteins that are co-ingested and interfere with digestive processes in the gut. Defensins inhibit α-amylase activity. Deaminases degrade amino acids. Proteinase inhibitors and peptidases inhibit the arthropod’s proteases. Peptidases, lectins and possibly some PR proteins damage the peritrophic membrane. Plant polyphenol oxidases in combination with plant phenolics are believed to generate quinones in the arthropod gut. These quinones may damage soluble and membrane proteins and DNA. Digestive processes of the herbivore are shown in red and counter-measures of the plant in green.