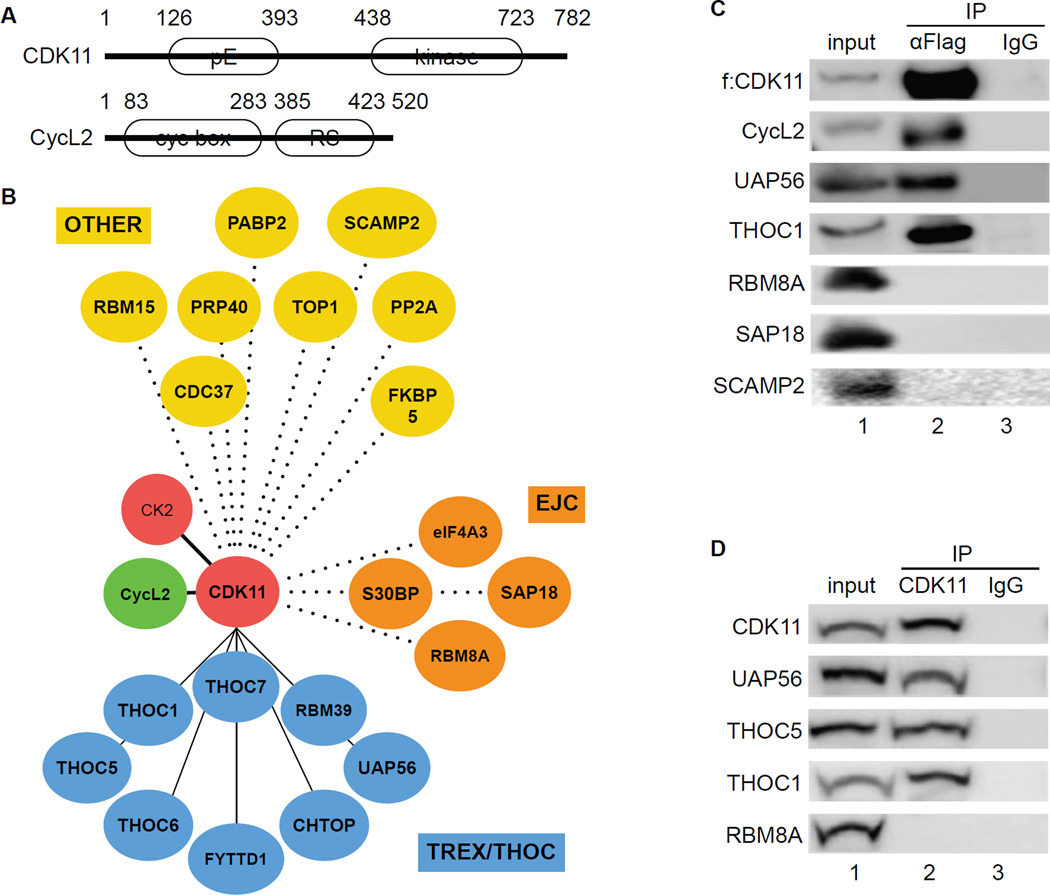
Figure 1. CDK11 associates with TREX/THOC in 293 T cells.
A. A schematic representation of CDK11 and CycL2. CDK11 contains 782 residues and migrates with an apparent molecular mass of 110 kDa. CycL2 contains 520 residues with an apparent molecular mass of 58 kDa. White ovals depict regions rich in glutamic acids (pE), the kinase domain of CDK11, cyclin boxes and the arginine-serine (RS)-rich domain in CycL2.
B. Dendrogram of the CDK11 proteome. Mass spectrometry of proteins that co-immunoprecipitated with CDK11 identified TREX/THOC (blue circles), EJC (brown circles) and various OTHER (yellow circles) proteins.
C. Co-immunoprecipitations of f:CDK11-interacting proteins. Immunoprecipitation of FLAG epitope-tagged CDK11 protein (f:CDK11) was followed by western blotting with anti-FLAG, UAP56, THOC1, CycL2, RBM8A, SAP18 and SCAMP2 antibodies. Lanes contain the following: lane 1, input; lane 2, co-immunoprecipitated proteins; lane 3, IgG control.
D. Co-immunoprecipitations between endogenous proteins. Immunoprecipitation of the endogenous CDK11 protein (CDK11) was followed by western blotting with anti-UAP56, THOC5, THOC1 and RBM8A antibodies (lanes 3–7). Lanes are as in panel C.