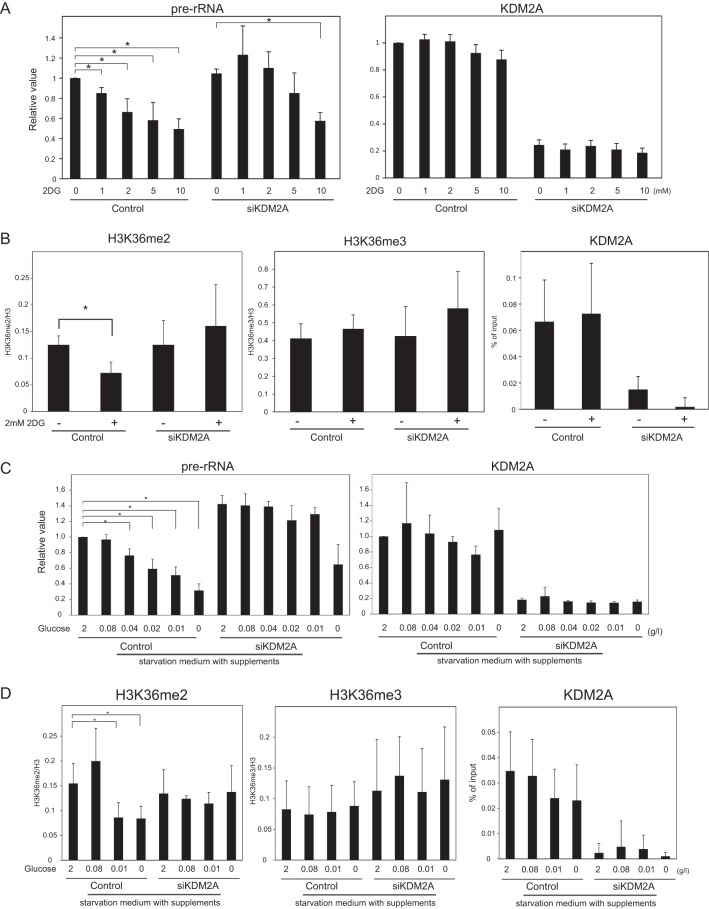
FIG 2.
KDM2A reduces rRNA transcription in mild glucose-starvation conditions. (A) Three days after transfection of control siRNA (control) or KDM2A siRNA (siKDM2A), MCF-7 cells were further cultured for 2 h in RPMI 1640 supplemented with 10% serum in the presence of 2DG at the indicated concentrations, and the amounts of pre-rRNA and KDM2A mRNA were measured by qRT-PCR. The expression levels were normalized by Polr2 mRNA. (B) Three days after transfection of siRNAs, the cells were further cultured for 2 h in RPMI 1640 supplemented with 10% serum in the presence or absence of 2 mM 2DG. ChIP analyses were performed to detect H3K36me2, H3K36me3, histone H3, and KDM2A in the rDNA promoter. The results of the histone modifications were expressed as the percentage of input normalized by the histone H3 values. The results of KDM2A were expressed as the percentage of input. (C) Three days after transfection of siRNAs, cells were further cultured for 2 h in various concentrations of glucose-containing DMEM supplemented with insulin, hypoxanthine, transferrin, and thymidine, and the amounts of pre-rRNA and KDM2A mRNA were measured by qRT-PCR. The expression levels were normalized by Polr2 mRNA. (D) Three days after transfection of siRNAs, cells were further cultured for 2 h in various concentrations of glucose-containing DMEM supplemented with insulin, hypoxanthine, transferrin, and thymidine. ChIP analyses were performed to detect H3K36me2, H3K36me3, histone H3, and KDM2A in the rDNA promoter. The results are expressed as in panel B. All experiments were performed at least three times, and mean values with the standard deviations are indicated. *, P < 0.05.