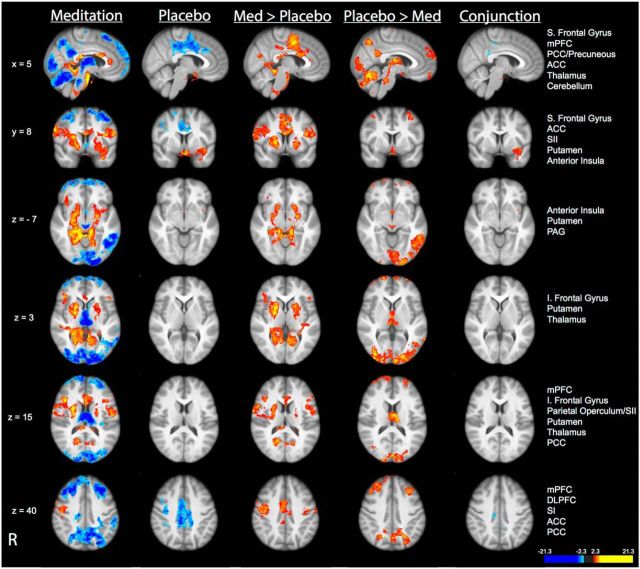
Figure 5.
Brain activations and deactivations associated with the main effect of mindfulness meditation and placebo. Compared with pre-manipulation, mindfulness meditation produced significant activation in the bilateral anterior insula cortices, putamen, inferior (I) frontal gyrus, SII, and SI corresponding to the nose and face. Mindfulness meditation was also associated with significant deactivation in the thalamus, PAG, mPFC, DLPFC, cerebellum and PCC/precuneous. Placebo was associated with deactivation in brain regions ranging from the midcingulate cortex to the ACC. Placebo produced significant activation in the left anterior insula compared with pre-manipulation. Compared with placebo, mindfulness meditation produced significantly greater activation in the ACC, bilateral anterior insula, right putamen, and SI of the nose and face. Compared with mindfulness meditation, placebo produced greater activation in the DLPFC, mPFC, thalamus, PAG, PCC/precuneous, and cerebellum. Conjunction analyses revealed significant overlapping activation between the main effect of mindfulness meditation and placebo at the border between the ventral insula and medial temporal lobe. Slice locations correspond to standard stereotaxic space.