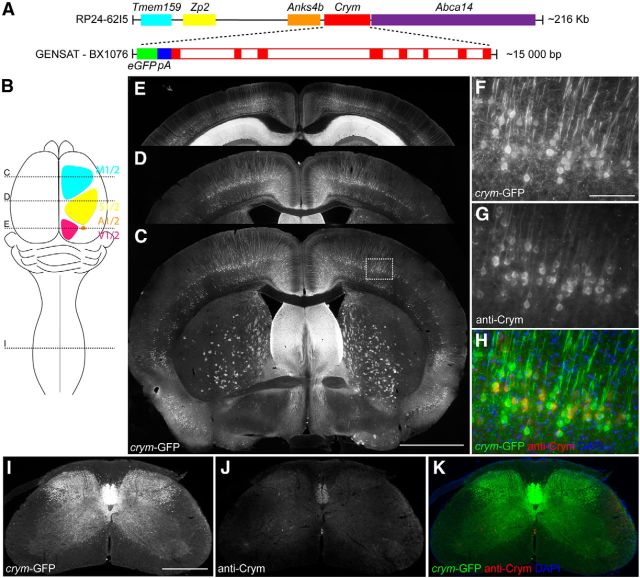
Figure 1.
BAC transgenic Tg(Crym-EGFP)GF82Gsat expresses soluble GFP in adult brain and spinal cord. Schematic (A) shows a linear representation of the BAC clone RP24-62I5, which contains Tmem159 (cyan), Zp2 (yellow), Anks4b (orange), Crym (red), and Abca14 (purple). Enlarged sequence shows inferred schematic of GENSAT clone BX1076, which contains EGFP (green) with its own PolyA (blue) 5′ to the start codon of Crym (red solid boxes are exons, open boxes are introns). BX1076 was injected into fertilized ova to create Tg(crym-EGFP)GF82 (crym-GFP) mice. Schematic (B) shows location of primary and secondary motor (cyan), sensory (yellow), auditory (orange), and visual cortex (magenta). Stippled lines labeled C, D, and I in schematic B indicate location of photomicrographs through the transverse plane of the brain (C–E) and cervical spinal cord (I–K) of an adult wild-type crym-GFP mouse. Intense GFP labeling is observed in layer V of motor (C, ∼0.86 mm anterior to bregma), sensory (D, ∼0.86 posterior to bregma), auditory and visual cortex (E, ∼3.5 mm posterior to bregma). GFP is additionally localized in a diffuse pattern in the striatum (C) and in the CA1 and CA2 regions of the hippocampus (E). High-power photomicrographs (F–H) show crym-GFP expression in pyramidal neurons in layer V of primary motor cortex. Antibodies to Crym label all crym-GFP+ pyramidal neurons (G, H). Low-power photomicrographs (I–K) of a transverse section of C7 spinal cord show robust crym-GFP expression in the dorsal, lateral, and ventral funiculi (I) and throughout dorsal and intermediate gray matter. Low levels of Crym protein are observed in the ventral dorsal column (J), which overlaps 100% with crym-GFP (K). Scale bars: C, 1 mm; F, 100 μm; I, 500 μm.