Figure 1.
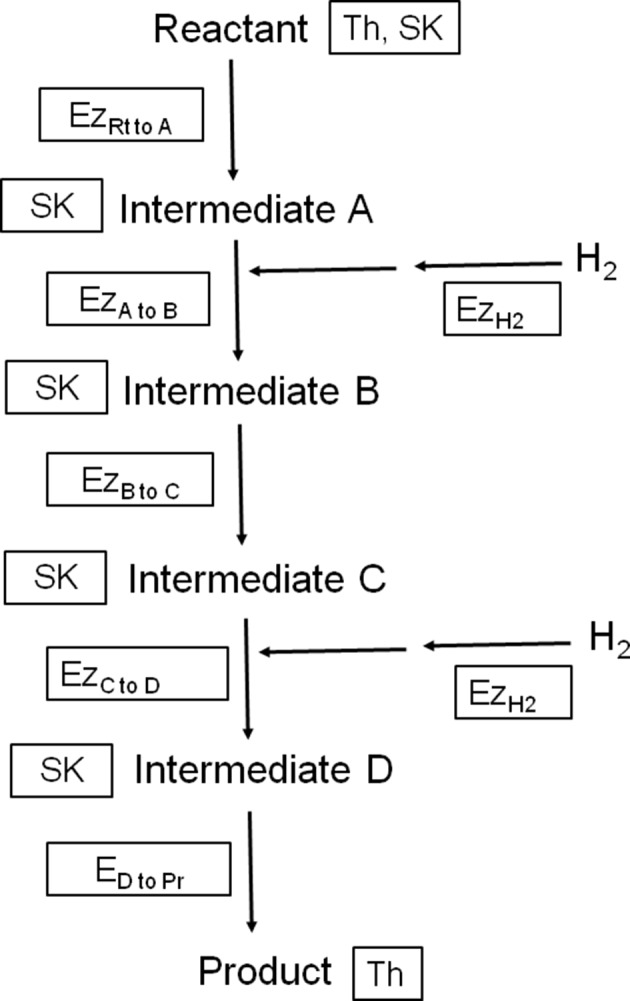
Illustration depicting three different means of physicochemical control of the rate of a fictitious H2-incorporating biochemical pathway starting with a reactant (Rt) that is converted into four intermediates A, B, C and D, and finishing with a product (Pr). Th, thermodynamic control, which depends on the activities of the reactant and product; Ez, enzyme kinetics control, which depends on the activity of the most limiting enzyme. Depicted in the diagram are two hydrogenases (EzH2) and five enzymes catalyzing conversions between carbon compounds (Ezxtoy); SK, substrate kinetics control, which depends on the concentration of the reactant or the most limiting intermediate and is not affected by product accumulation.
