Figure 1.
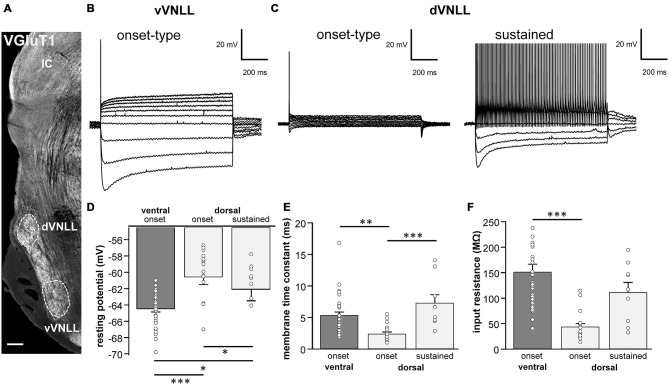
Intrinsic properties differ between vVNLL and dVNLL neurons. (A) Low-power image with VGluT1-labeling illustrates the relative location of the VNLL within the auditory brainstem. The dorsal and ventral parts of the VNLL (dVNLL and vVNLL, respectively) are marked with a dashed line to show the respective recording sites. Scale bar: 200 μm. (B) Representative voltage responses to hyperpolarizing and depolarizing current injections recorded from vVNLL neurons. Depolarizing current injections elicited an onset-type firing pattern in vVNLL neurons. (C) Depolarizing current injections elicited different types of firing patterns in dVNLL neurons: onset-type (left) and sustained (right) firing pattern. (D) Resting potential, (E) membrane time constant and (F) peak input resistance for vVNLL and dVNLL neurons. dVNLL: onset-type n = 19, sustained n = 9, vVNLL: onset-type n = 34. Data are obtained from twelve C57/Bl6J mice. Statistical significance was determined by a single-factor ANOVA test followed by a Scheffé’s post hoc test; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.