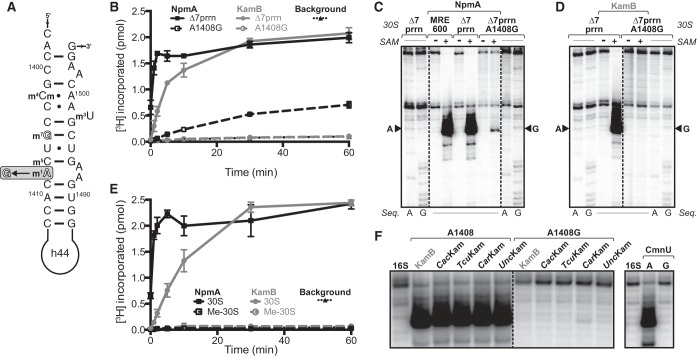
FIG 1.
NpmA methylates 30S subunits with G1408. (A) Sequence and secondary structure of the h44 region containing the target nucleotides (outline font) of the m7G1405 and m1A1408 aminoglycoside-resistance 16S rRNA methyltransferases. The mutation in the 30S-A1408G subunit (shaded box) used in this study and the locations of intrinsic 16S rRNA modifications in this region are also indicated. (B) In vitro methylation in the presence of [3H]SAM of Δ7prrn wild-type and 30S-A1408G subunits by NpmA (black) and KamB (gray). NpmA, but not KamB, can methylate 30S-A1408G subunits (dashed black line). (C and D) RT analysis of 16S rRNA methylation by NpmA (C) and KamB (D) using 30S subunits from E. coli MRE600 (A1408), Δ7prrn (A1408), and Δ7prrn-A1408G. Sequencing lanes (Seq.) contain the complementary dideoxynucleotide in the RT reaction. The position of modified 1408 is marked by arrowheads. (E) In vitro methylation in the presence of [3H]SAM of wild-type unmethylated (30S) and m1A1408 premethylated (Me-30S) subunits by NpmA (black) and KamB (gray). (F) RT analysis of modification of wild-type or 30S-A1408G subunits by five other 16S rRNA (m1A1408) methyltransferases (13, 14); each enzyme is capable of incorporating only the m1A1408 modification. The origins of the enzymes not described in the text are Catenulispora acidiphila (CacKam; UniProt accession C7Q5P8), Thermomonospora curvata (TcuKam; D1A6K4), Candidatus Arthromitus sp. SFB-mouse-NYU (CarKam; F9VLU6), an uncultured bacterium (UncKam; K2DC64), and Saccharothrix mutabilis subsp. capreolus (CmnU; A6YEH1).