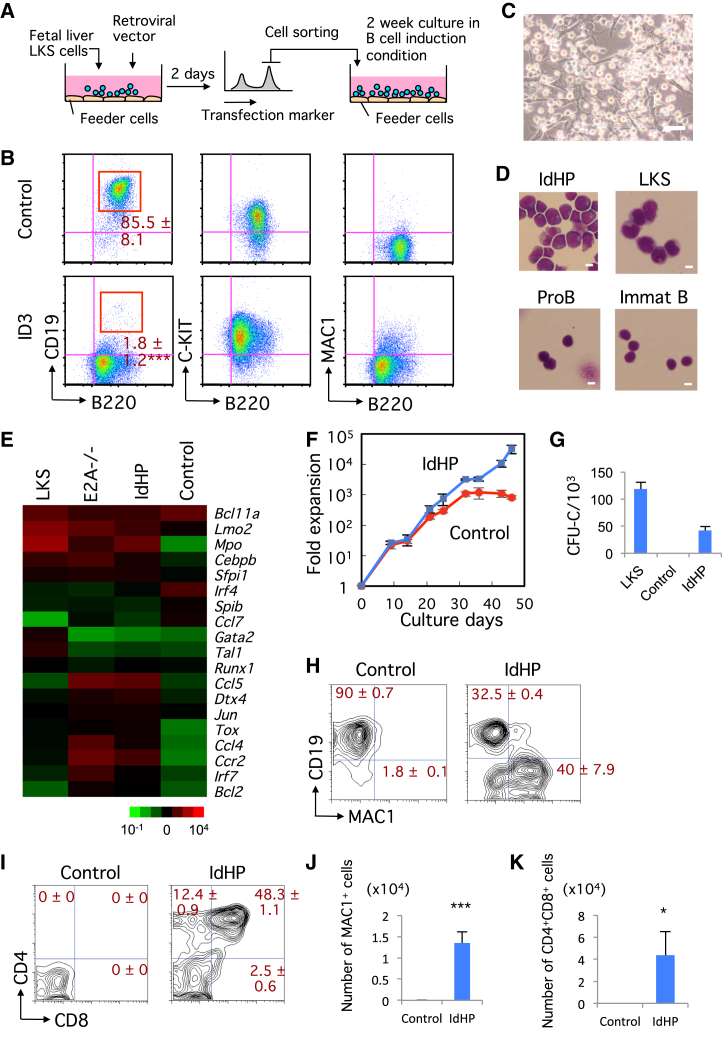
Figure 1.
Generation of IdHP Cells from Murine HSCs or HPCs
(A) Schematic representation of IdHP cell generation.
(B) Flow cytometric analysis of control (empty vector) and ID3-overexpressing FL progenitor cells (n = 3).
(C) Photomicrograph of IdHP cells. Scale bar, 10 μm.
(D) Wright’s staining of IdHP cells, LKS cells, pro B cells, and immature B (Immat B) cells from BM. Scale bars, 10 μm.
(E) Microarray analysis of gene expression in LKS cells, E2A−/− HPCs, IdHP cells, and pro B cells derived from cultures of control vector-expressing FL progenitors.
(F) In vitro expansion of IdHP and control cells. Viable cells were counted at an each time point (n = 3).
(G) CFU-C assay of LKS, control, and IdHP cells (n = 3).
(H) Myeloid and B cell generation from IdHP cells in vitro. Flow cytometric profiles of IdHP cells cultured on TSt-4 stromal cells for 14 days are shown (n = 3).
(I) T cell generation from IdHP cells in vitro. Flow cytometric profiles of control and IdHP cells cultured on TSt-4/DLL1 stromal cells for 12 days are shown (n = 3).
(J) The number of MAC1+ cells generated from IdHP and control cells on TSt-4 stromal cells is shown (n = 3). The FACS profile from IdHP cells is shown in (H).
(K) The number of CD4+CD8+ cells generated from IdHP cells on TSt-4/DLL1 stromal cells is shown (n = 3). The FACS profiles are shown in (H) and (I). Student’s t test, ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗∗p < 0.001. Data are shown as mean ± SD from three independent experiments.
See also Figure S1.