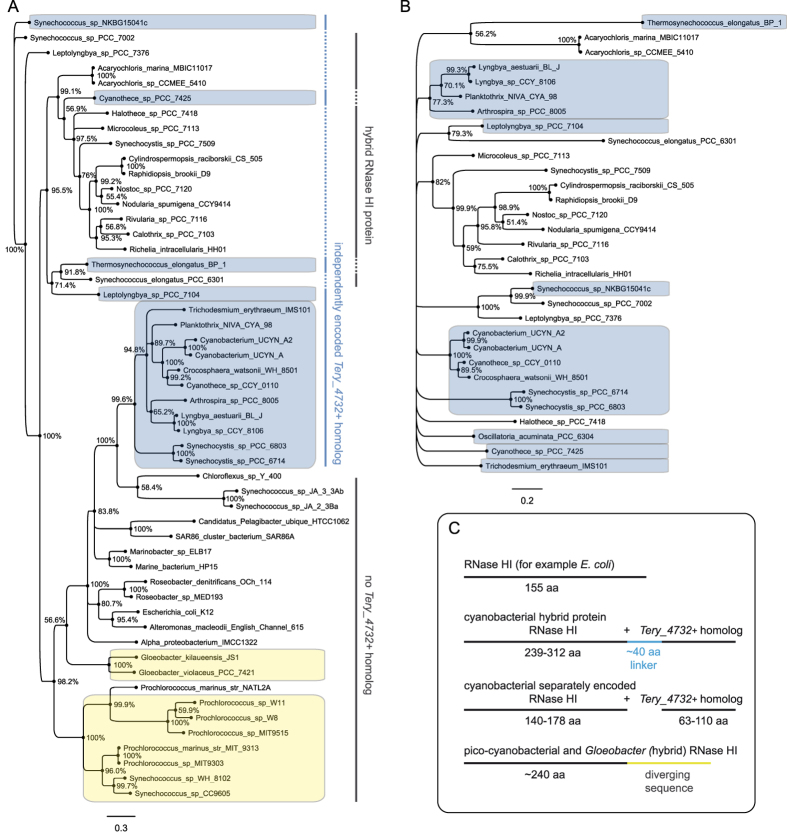
Figure 2. Phylogeny of homologs of the RNase HI gene and the twintron host gene.
Separate Bayesian trees showing the phylogenetic relationships of solitary and hybrid RNase HI gene homologs (A) and Tery_4732+ homologs (B). Percentages at each node are posterior probabilities for the existence of that node, as inferred by Mr. Bayes42. Those species containing independently encoded RNase HI and Tery_4732+ homologs are in blue boxes. The yellow boxes mark species with an RNase HI carrying a 3′extension that is not homologous to Tery_4732+. (C) Schematic comparison of RNase HI genes and RNase HI hybrid genes in cyanobacteria, picocyanobacteria and other bacteria (represented by E. coli). Cyanobacterial hybrid RNase HI proteins contain a non-conserved linker sequence of approximately 40 amino acids (blue) between the two domains representing RNase HI and the Tery_4732+ homolog, respectively.