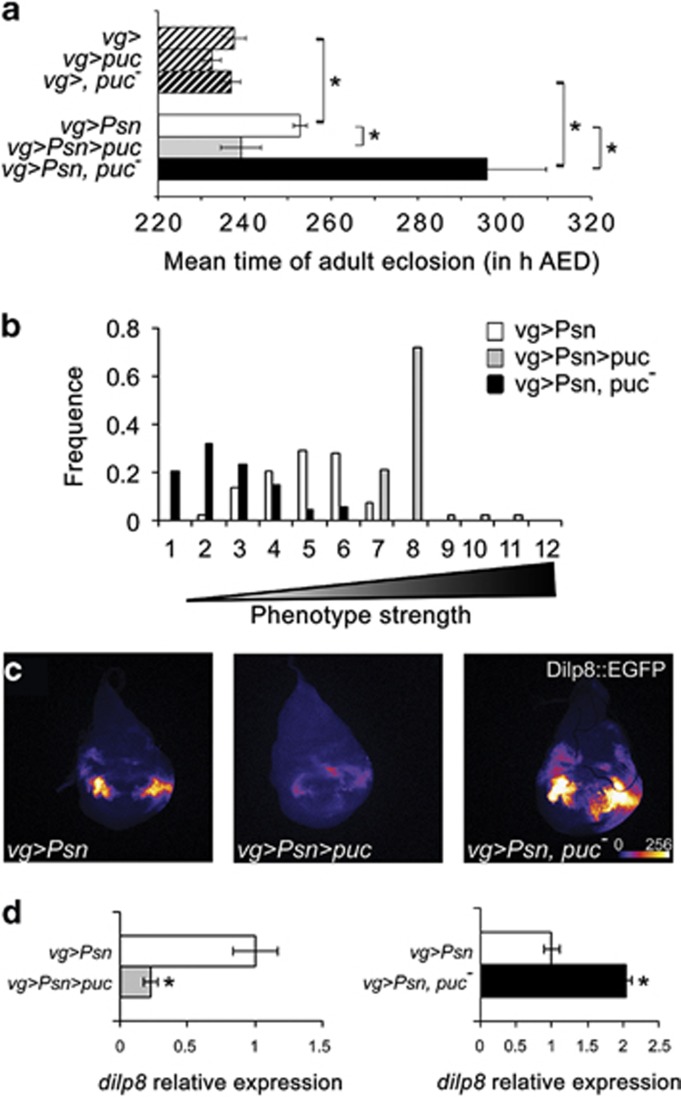
Figure 4.
The JNK pathway regulates a Dilp8-dependent developmental delay. (a) Effects of puc overexpression (UAS-puc) (gray) and puc mutant heterozygosity (pucE69/+) (black) compared with control (white) in a vg-GAL4, UAS-Psn, UAS-Psn/+ (plain bars) or vg-GAL4/+ (hatched bars) background on the mean time of adult eclosion. Error bars represent the S.E.M. (n=4). Asterisks indicate significant difference (P<10−4, ANOVA). (b) Distribution of notched-wing phenotypes of vg-GAL4, UAS-Psn, UAS-Psn/+ UAS-puc/+ (gray bars) and vg-GAL4, UAS-Psn, UAS-Psn/+ pucE69/+ (black bars) flies compared with vg-GAL4, UAS-Psn, UAS-Psn/+ flies (open bars). (c, d) Intensity of GFP reflecting dilp8 expression in vg-GAL4, UAS-Psn, UAS-Psn/+ dilp8MI00727/+ (c left, d white bars), vg-GAL4, UAS-Psn, UAS-Psn/+ dilp8MI00727/UAS-puc (c center, d gray bar), and vg-GAL4, UAS-Psn, UAS-Psn/+ dilp8MI00727/pucE69(c right, d black bar) third-instar wing imaginal discs. Error bars represent the S.E.M. of at least eight independent experiments. Asterisks indicate significant difference (P<10−3, ANOVA)