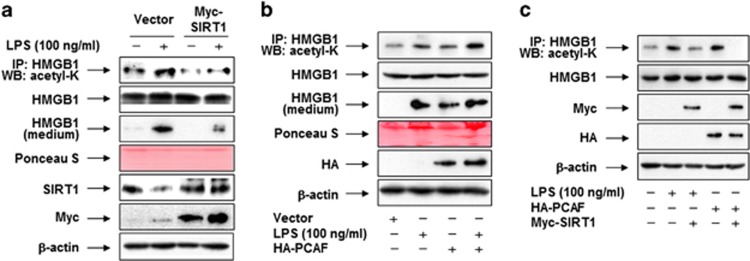
Figure 7.
SIRT1-mediated deacetylation of HMGB1 is a critical factor in the PPAR-δ/γ–mediated inhibition of HMGB1 release. (a) RAW 264.7 cells were transfected with empty vector (pcDNA3.1/Myc) or pcDNA3.1-Myc-SIRT1. (b) Cells were transfected with empty vector (pcDNA3.1/HA) or pcDNA3.1-HA-PCAF. (c) Cells were transfected with empty vector (pcDNA3.1), pcDNA3.1-Myc-SIRT1, or pcDNA3.1-HA-PCAF. After incubation for 38 h, cells were maintained in serum-free medium for 24 h, and then stimulated with or without LPS for 6 h (for detection of acetyl-HMGB1) or 24 h (for detection of released HMGB1). Cell lysates were pulled down with anti-HMGB1 and immunoblotted with anti-acetyl-lysine to detect acetylated HMGB1. Each membrane was then stripped and re-probed for HMGB1, as a loading control. For determination of released HMGB1, equal volumes of conditioned media were subjected to Western blot analysis; Ponceau S staining was used as a loading control. Whole-cell lysates were subjected to western blot analysis with an anti-HMGB1, anti-SIRT1, anti-Myc, or anti-HA antibody, as appropriate, to determine the expression levels of HMGB1 and SIRT1 (a and c) or PCAF (b and c)