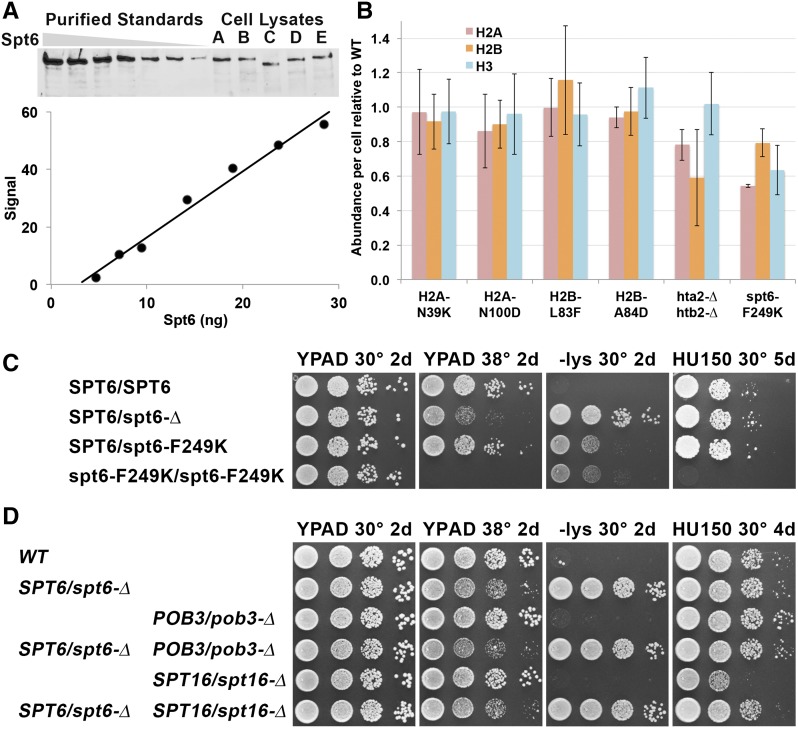
Figure 4.
Spt6 is abundant and displays haploinsufficiency. (A) Western blots using polyclonal antiserum against Spt6 were used to detect purified protein or protein extracted from strains A–E (see Table 1; C has the spt6-50 mutation that lacks the C-terminal domain and therefore produces a shorter protein). Quantitation of the standards is shown below the Western blot; the response was linear in this case but does not pass through the origin, indicating the necessity of using a standard curve to determine an accurate assessment of the amount of Spt6 in the lysates. (B) The amounts of H2A, H2B, and H3 were tested by Western blotting. In this case, a set of dilutions of lysates from a strain with WT histone genes (with the same genetic markers as the mutation being tested downstream of the genes) was used as a standard, and each histone level was normalized to the WT value. Error bars indicate the standard error of at least four measurements (two biological replicates with at least two Western blots each). (C and D) Diploids with the genotypes shown (Table 1) were tested for phenotypes as in Figure 1.