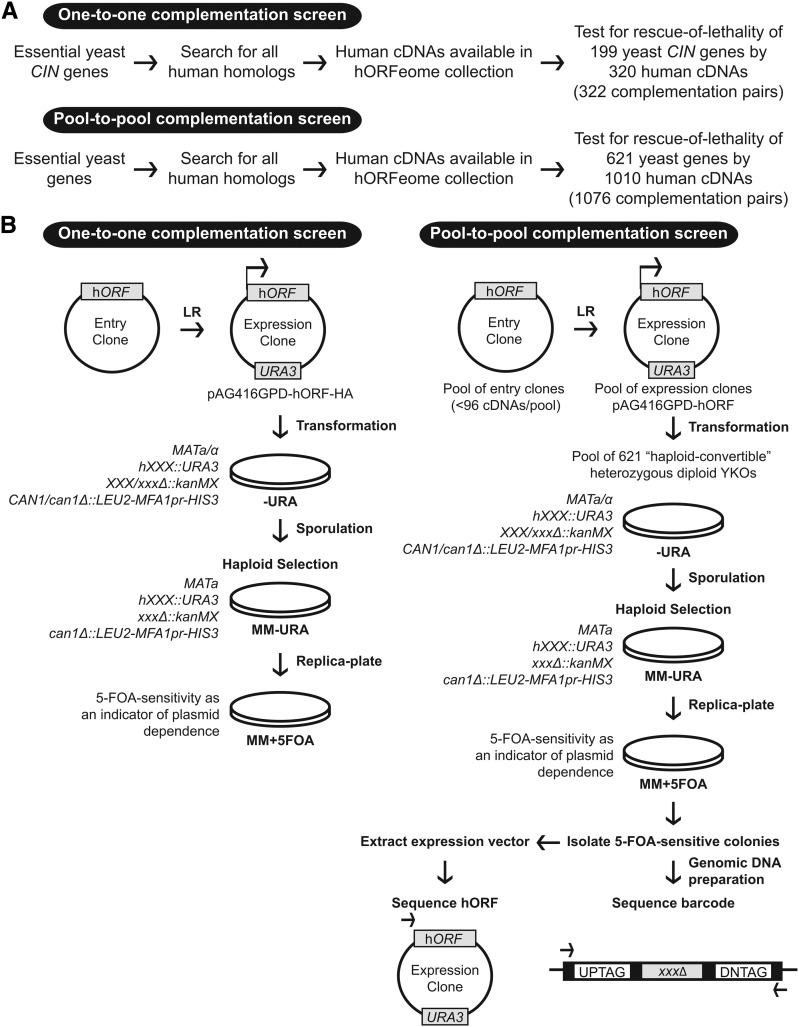
Figure 1.
Overview of the experimental design for the complementation screens. (A) Pipeline outlining which human–yeast complementation pairs were included in both screens. (B) Flowchart for the complementation screens. Human cDNAs were shuttled from entry clones to indicated yeast destination vectors to generate yeast expression vectors. Single or pooled expression vectors were then transformed to matched or pooled haploid convertible heterozygous diploids and maintained on −Ura media. Following sporulation, heterozygous diploids were plated on haploid selection media (MM −Ura). “Rescued” haploids were tested for plasmid dependency by replica plating on MM +5-FOA. For the pooled screen, 5-FOA-sensitive colonies were isolated for sequencing of yeast barcode and expression vectors.