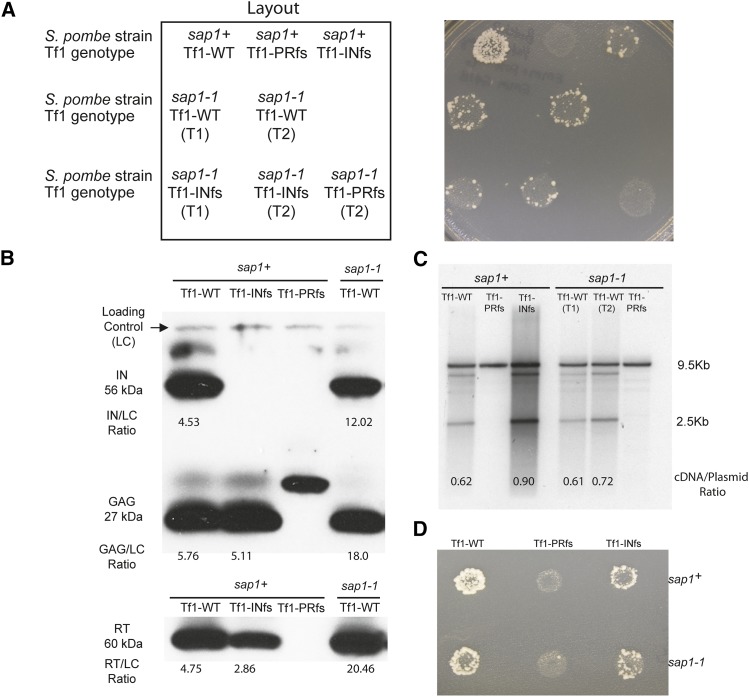
Figure 1.
(A) Tf1 retrotransposition is reduced in S. pombe with a temperature-sensitive sap1-1 allele. The results of transposition patch assays of wild-type S. pombe (sap1+) and of S. pombe harboring a temperature sensitive allele of sap1 (sap1-1). Tf1-PRfs, protease frameshift Tf1 mutant; Tf1-INfs, IN frameshift Tf1 mutant. Patches in which the expression of Tf1 was induced were first replica printed to plates containing 5-FOA and then printed to plates with 5-FOA and G418. T1 and T2 indicate two individual transformants. (B) Immunoblot analysis of Tf1 Gag, IN, and RT in wild-type (sap1+) and sap1-1 mutant S. pombe extracts. Polyclonal antibodies specific for IN, Gag, and RT detected the mature 56-kDa IN, 27-kDa Gag, and 60-kDa RT species. “Loading control” indicates a nonspecific band used for the normalization of IN, Gag, and RT with ImageJ. The numbers represent the ratio of the intensity of the indicated band to the loading control. The frameshift transposons used in this experiment are the same as those listed in A. (C) DNA blot analysis of total DNA extracted from wild-type (sap1+) and sap1-1 mutant S. pombe cells and digested with BstXI. Blots were probed with a randomly labeled 1-kb BamHI fragment containing the neo sequence. The large 9.5-kb fragment resulting from the digestion of the Tf1 donor plasmid served as the loading control for comparing levels of the 2.5-kb cDNA. Numbers indicate the ratio of the intensities of the indicated cDNA band to the loading control. (D) To measure recombination, cells were replica printed to plates with 5-FOA and then printed to plates with 5-FOA and G418.