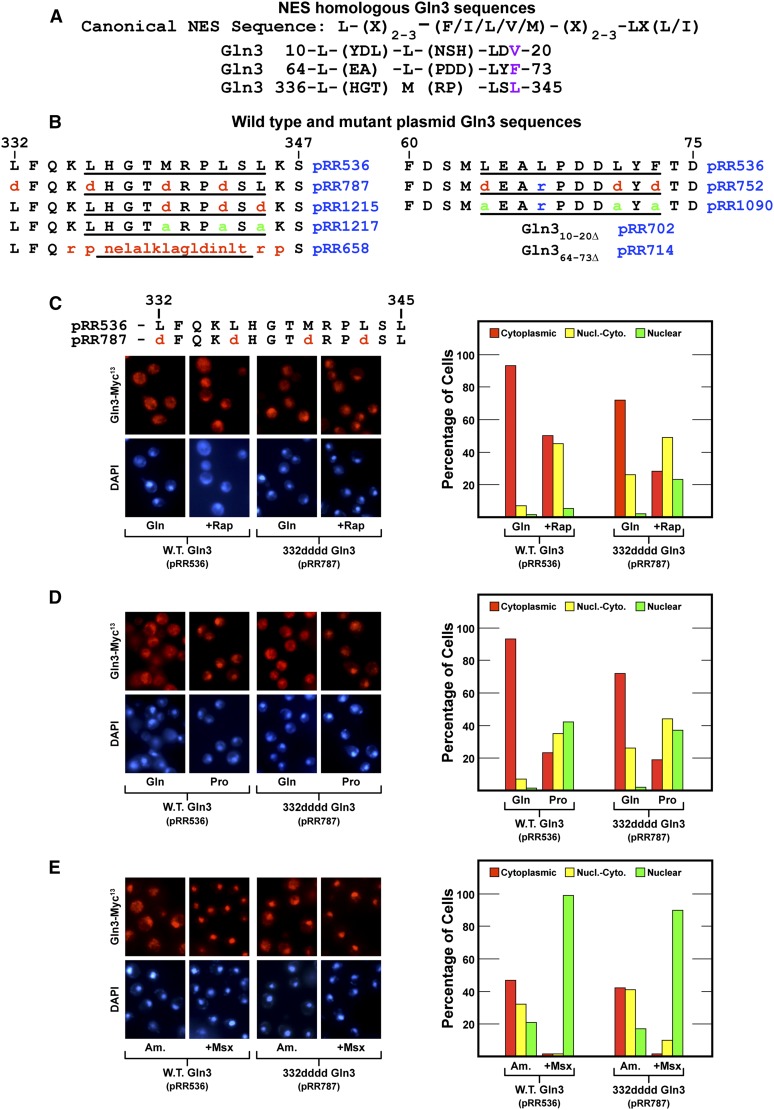
Figure 1.
(A) Amino acid sequences of wild-type Gln3 that are homologous with the canonical NES in the sequence used by Carvalho and Zheng (2003). (B) Wild-type (pRR536) and substitution mutant plasmid sequences of Gln3 regions homologous with NESs. Gln3 amino acid coordinates appear above the sequences. (C–E) Gln3-Myc13 export is not demonstrably affected by amino acid substitutions in and adjacent to the previously reported Gln3 NES. Wild-type (pRR536) and Gln3L332D,L336D,M340D,L343D-Myc13 (pRR787) mutant cells were grown in YNB-glutamine (C and D, Gln), YNB-proline (D, Pro), or YNB-ammonia (E, Am) medium to mid-log phase (A600nm = 0.5). Samples were removed for assay of Gln3-Myc13 localization. Rapamycin (C, +Rap) or methionine sulfoximine (E, +Msx) was added where indicated. After incubation (20 and 30 min, respectively), the cultures were again sampled for assay. The intracellular distributions of Gln3-Myc13 were determined as described in Materials and Methods. The precision of Gln3-Myc13 scoring in the three categories we used is described in Materials and Methods. Representative microscopic images of fields from which the histograms were obtained are shown to the left of each set of histograms.