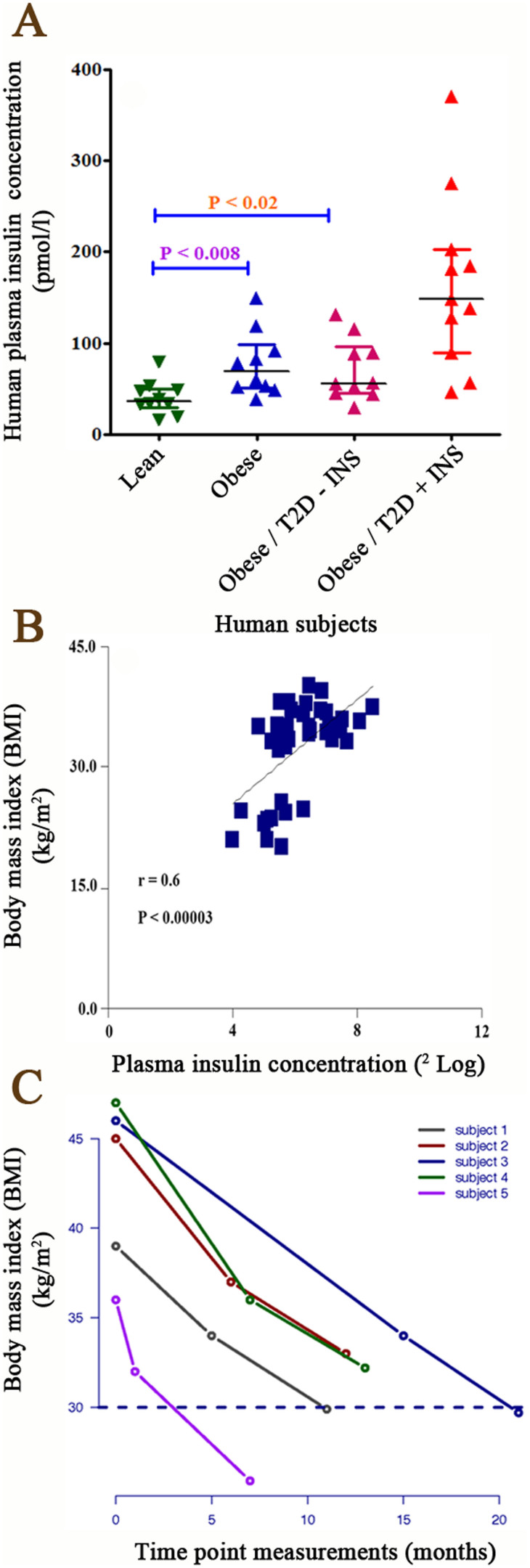
Figure 6.
(Panel A). DAKO insulin ELISA kit was applied to measure insulin concentrations in the plasma of 41 human subjects categorized in four groups based on Body Mass Index (BMI); 1- Lean subjects (BMI, 20.1–25.6, only one patient above 25), 2- Obese subjects (BMI, 32.5–39.5), 3-Obese subjects with type 2 diabetes (T2D) without receiving insulin (BMI, 32.1–40) and obese subjects with T2D, receiving insulin (BMI, 33.3–38). BMI is expressed as mass (kg)/(height (m))2. The p-value resulted from one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). P < 0.05 was accepted as statistically significant. Insulin concentrations were expressed as pmol/l shown in Y-axis. (Panel B). Correlation between plasma insulin concentrations (n = 41 human subjects) and Body Mass Index (BMI). BMI is expressed as mass (kg)/(height (m))2. The p-value resulted from one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). P < 0.05 was accepted as statistically significant. Insulin concentrations were expressed as pmol/l shown in Y-as and BMI was expressed as2log shown in X-axis. There was a strong positive correlation between plasma insulin concentration and human BMI (P < 0.00003, r = 0.6). (Panel C). The bariatric surgery of 5 human subjects with type 2 diabetes. The BMI (fat reduction) was measured three times in 5 patients; 1- before bariatric surgery is considered as basis point, 2- after surgery (depends on the date of surgery) and 3- the last measurement point (6 months after the second measurement). BMI was sharply decreased after the surgery. The BMI was calculated as Kg/m2 shown in Y-axis. The time point 0 is considered as before surgery. The X-axis shows the BMI measurements in different time points.