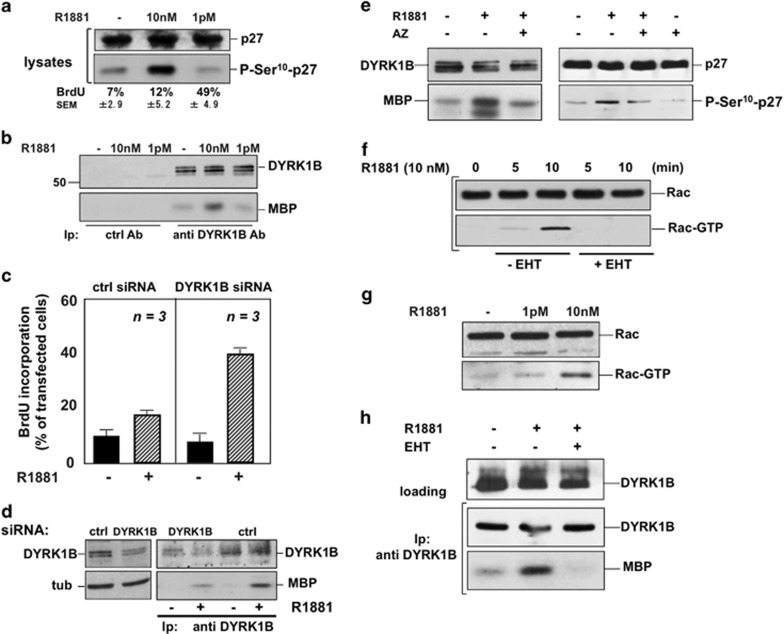
Figure 4.
Ten nanomolar androgen activation of DYRK 1B induces quiescence through p27 Ser10 phosphorylation and is Rac-dependent. NIH3T3 cells were used. In (a), quiescent cells were untreated or treated for 30 min with 10 nM or 1 pM R1881. Lysate proteins were analyzed by western blot, using antibodies against the indicated proteins (lysates). The lowest section shows the corresponding BrdU incorporation analyzed by IF and expressed as % of cells. Means and S.E.M. are shown. In (b), quiescent cells were untreated or treated for 30 min with 10 nM or 1 pM R1881. Lysate proteins were immunoprecipitated with control (ctrl) or anti-DYRK 1B antibody. Immune complexes were analyzed for DYRK 1B activity using myelin basic protein (MBP) as a substrate. DYRK 1B levels in immune complexes were detected by immunoblot with anti-DYRK 1B antibody. Quantitative analysis of 10 nM R1881-triggered DYRK 1B activity from three different experiments was analyzed using the NIH Image J program. It showed a fivefold increase in kinase activity. In contrast, no significant increase in kinase activity was detected in cells stimulated with 1 pM R1881. In (c), growing cells were transfected with non-targeting siRNA (ctrl siRNA) or DYRK 1B siRNA (DYRK 1B siRNA). Cells were co-transfected with negative control siRNA Alexa-Fluor 488 to help identification of transfected cells. After transfection, cells were made quiescent, then left unstimulated or stimulated for 18 h with 10 nM R1881. After in vivo pulse with BrdU, BrdU incorporation was analyzed by IF and expressed as % of transfected cells. Data are derived from at least 300 scored cells for each experiment. Means and S.E.M. are shown. Lysate proteins from cells transfected with non-targeting (ctrl) or targeting (DYRK 1B) siRNA were analyzed by western blot with anti-DYRK 1B antibody (left panel in d), and filter was re-probed with anti-tubulin antibody, as a loading control (tub). DYRK 1B was immunoprecipitated from the same lysate proteins and its activity in immune complexes was assayed using MBP as a substrate (right panel in d). In (e), quiescent cells were left untreated or treated for 30 min with 10 nM R1881, in the absence or presence of the DYRK 1B inhibitor AZ191, which was added (1 μM) 15 min before hormonal stimulation. Control cells in right panel were treated with the inhibitor alone. In left panels, lysate proteins were immunoprecipitated with anti-DYRK 1B antibody. Immune complexes were analyzed for DYRK 1B activity using MBP as a substrate. DYRK 1B levels in immune complexes were detected by immunoblot with anti-DYRK 1B antibody. In right panels, lysate proteins were analyzed by western blot, using antibodies against the indicated proteins. In (f), quiescent cells were left untreated or treated for the indicated times with 10 nM R1881, in the absence or presence of the Rac inhibitor EHT1864 (at 10 μM), which was added 2 h before hormonal stimulation. Rac pull-down assay was performed and the amounts of total Rac and Rac-GTP were detected by western blot. In (g), quiescent cells were untreated or treated for 10 min with 1 pM or 10 nM R1881. Rac pull-down assay was performed as in (f). In (h), quiescent cells were untreated or treated for 30 min with 10 nM R1881 in the absence or presence of EHT1864 (10 μM). Lysate proteins containing the same amount of DYRK 1B (loading) were incubated with anti-DYRK 1B antibody. The lower section shows DYRK 1B activity in immune complexes, assayed using MBP as a substrate. The upper section shows the western blot of immune complexes with anti-DYRK 1B antibody