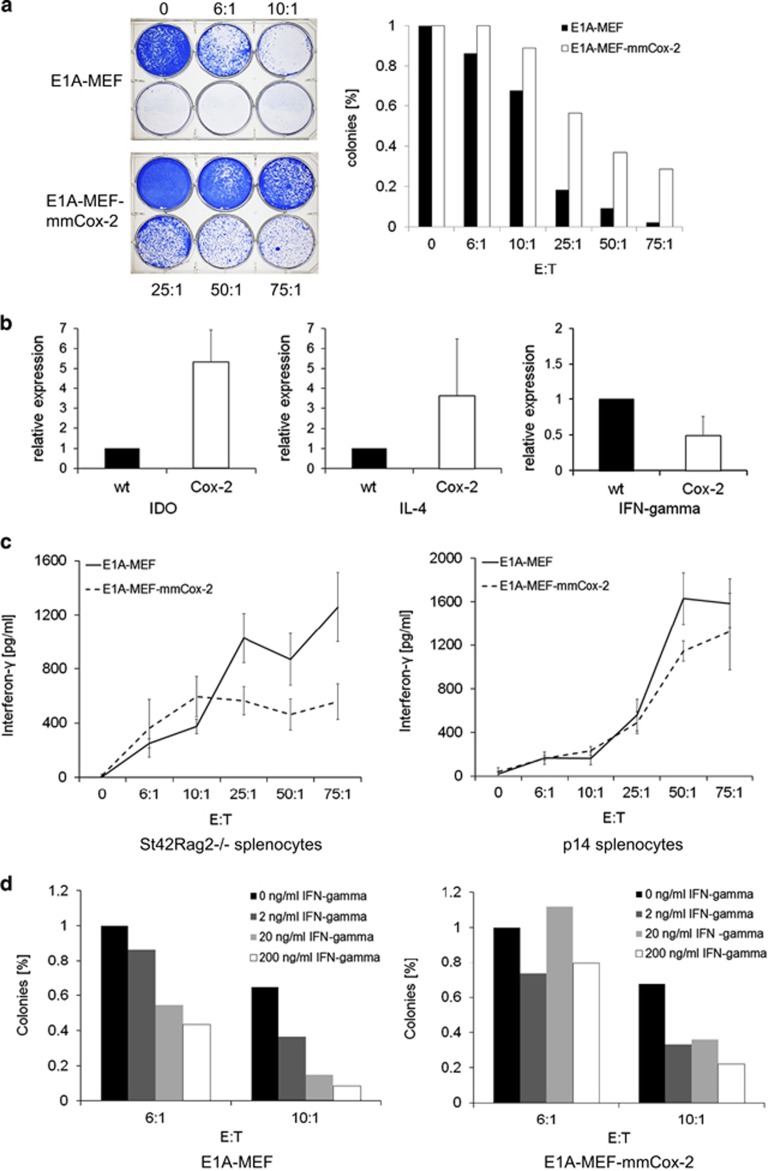
Figure 4.
COX-2 blunts the release of interferon-gamma by antigen-activated T cells. (a) Clonogenic survival of E1A-MEF and E1A-Cox2-MEF loaded with the LCMV gp33 peptide following incubation with gp33-specific p14 splenocytes. A representative photograph (left panel), and enumeration of colonies normalized to medium control (mean values) of three independent experiments each are shown (right panel). (b) Transcriptional expression levels of Il-4 and Ido1 are increased in tumors overexpressing Cox-2 while the expression of interferon-gamma is down regulated. Ex vivo RT-PCR analysis of tumors from E1A-MEF and E1a-Cox-2-MEF using specific primers for Il-4, Ido1 and interferon-gamma. Expression levels were normalized to actin. (c) Release of interferon-gamma by St42Rag2−/− splenocytes (left panel) or p14 splenocytes (right panel) incubated with E1A-MEF (solid lines) or E1A-Cox2-MEF (dashed lines). Prior to incubation with p14 splenocytes the MEF were loaded with LCMV gp33 peptide. Mean values (± SEM) of three independent experiments. (d) Clonogenic survival of E1A-MEF (left panel) or E1A-mmCox2-MEF (right panel) following incubation with St42Rag2−/− splenocytes at indicated effector-to-target ratios in the presence of increasing concentrations of recombinant murine interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma). Colonies were enumerated and normalized to the colony number in the absence of IFN-gamma