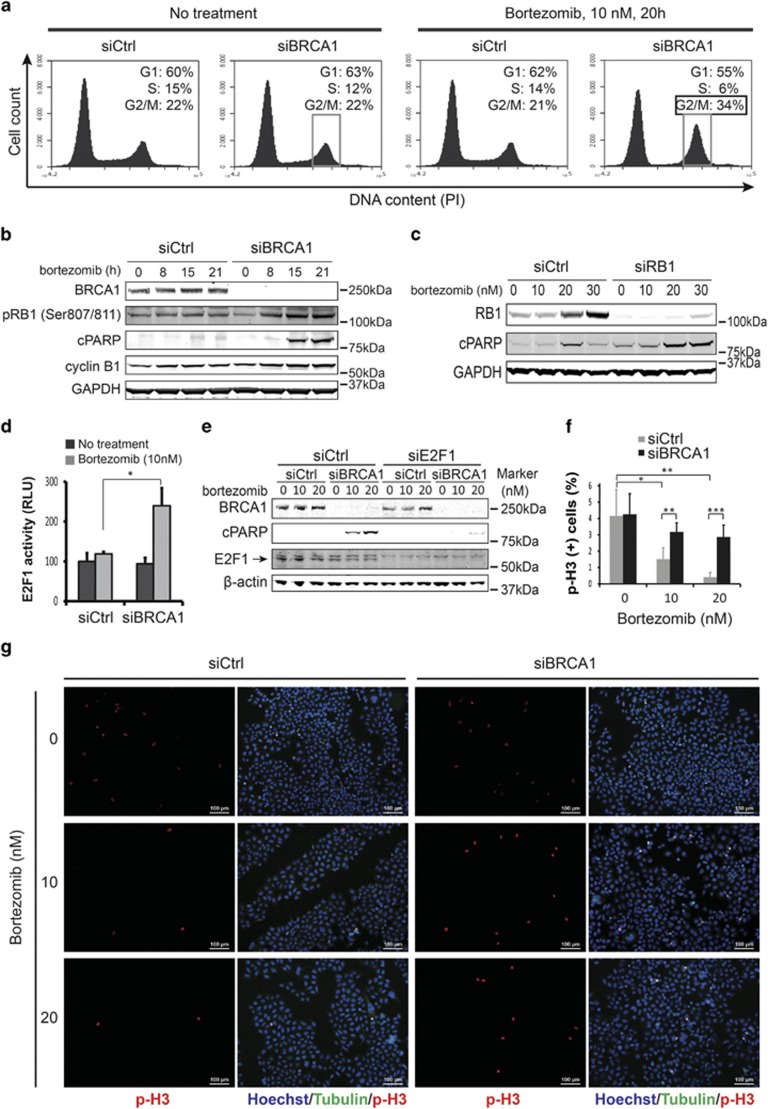
Figure 3.
Bortezomib affects both G1/S and G2/M cell cycle checkpoints in BRCA1-depleted cells. (a) HeLa cells treated with BRCA1 siRNA (siBRCA1) and 10 nM bortezomib for 20 h are accumulated in the G2 phase of the cell cycle, whereas the number of cells at G1 is reduced. Note that none of these treatments alone had any significant effect on the cell cycle profile. The G2/M fraction is marked with a frame. (b) Western blot showing that prolonged treatment of BRCA1-depleted cells with 10 nM bortezomib induced hyperphosphorylation of RB1, accumulation of cyclin B1, and cleaved PARP (cPARP), indicating induction of apoptosis. (c) Western blot showing that, similar to BRCA1, depletion of RB1 alone also leads to induction of apoptosis after bortezomib treatment. (d) E2F1 reporter activity was measured in HeLa cells transfected with control siBRCA1 and treated with bortezomib. Reporter activity without bortezomib treatment was used as a reference. Error bars indicate S.E.M. from duplicates. (e) Western blot demonstrating that knockdown of E2F1 rescues bortezomib-induced apoptosis in BRCA1-depleted cells as judged by a reduction in cPARP level. (f and g) Immunofluorescence (IF) staining for phosphorylated histone H3 (p-H3) marking mitotic cells reveals that depletion of BRCA1 allows for aberrant entry into mitosis after bortezomib treatment. Example IF images and quantification of p-H3-positive cells are shown in (g and f), respectively. Error bars represent S.D. with N=6 for siControl and N=8 for siBRCA1. Statistically significant differences are labeled with asterisks. RLU, relative luciferase unit