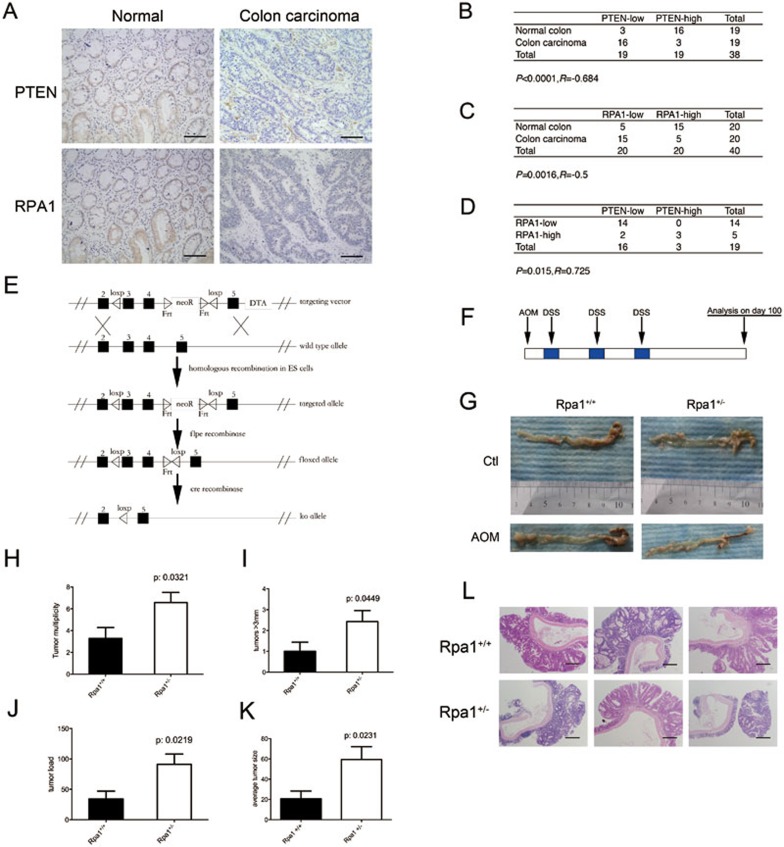
Figure 5.
RPA1 is important for suppression of colorectal carcinoma. (A) Immunohistochemical staining of PTEN and RPA1 in representative colon carcinoma specimens and matched normal colon specimens. Staining (brown) represents positive immunoreactivity. Scale bars, 50 μm. (B, C) PTEN (B) and RPA1 (C) protein expression status in normal colon and colon carcinoma specimens. (D) Correlation of PTEN and RPA1 protein levels in human colon cancers. Statistical significance in B-D was determined with the χ2-test. R is the correlation coefficient. (E) Schematic diagram of strategy for conditional knockout of murine Rpa1. (F) Sketch outlining the AOM/DSS-induced CRC model. Rpa1+/+ and Rpa1+/− mice were treated with or without AOM, which was given once, followed by periodic administration of DSS in water. n = 7 per group. (G-L) Following euthanasia, macroscopic (G) and microscopic (L) analyses of tumor were conducted. Scale bars, 100 μm. Statistical analyses of numbers of tumors (multiplicity, H), numbers of tumors > 3 mm (I), tumor volume (load, J) and average size (K) in two groups.