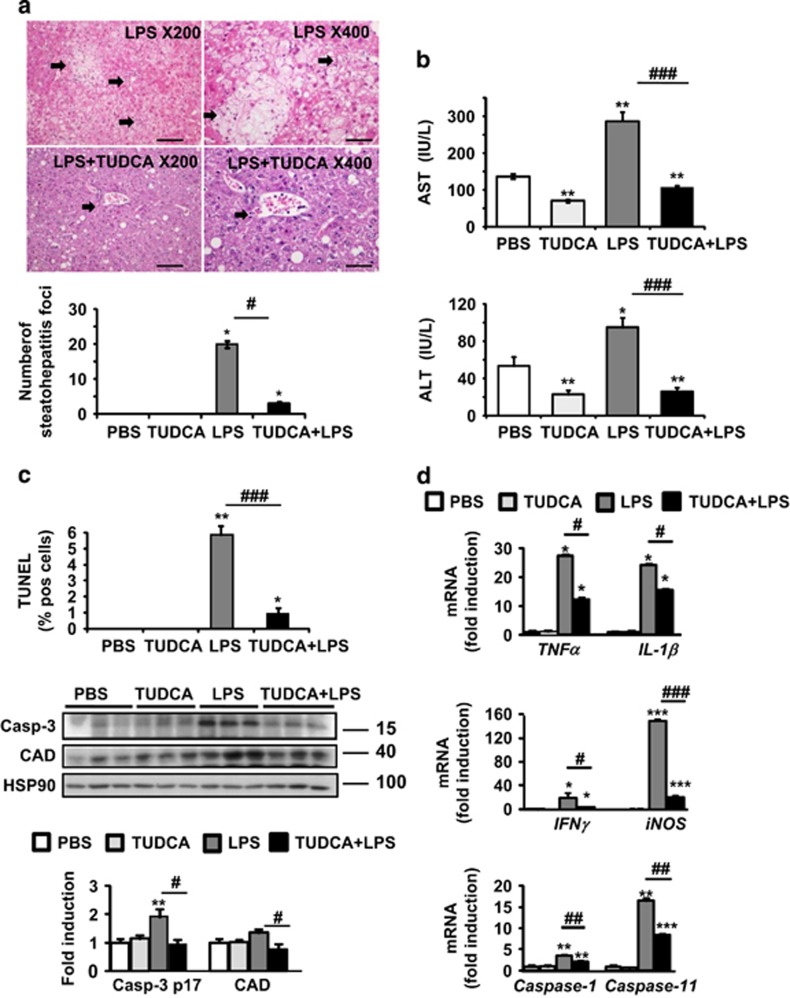
Figure 1.
TUDCA protected against LPS-induced liver injury, apoptosis and inflammasome priming in ob/ob mice. TUDCA was injected intraperitoneally (500 μg/g) for 5 days. An LPS challenge (2 μg/g) was performed 6-h before killing. (a) Shown are photomicrographs of sections of murine liver stained with H&E (scale bar=50 μm at × 200 or 25 μm at × 400 magnification). The number of steatohepatitis foci (number of inflammatory foci in contact with ballooned hepatocytes, identified by arrows) was evaluated. (b) Serum AST and ALT transaminase levels were measured (n=9–12). (c) Apoptotic hepatocytes were visualized with TUNEL assay. The expression of active caspase-3 and CAD was evaluated in total liver lysates. Quantification was performed from the immunoblot analysis and expressed as fold induction (n=6). (d) Relative expression of hepatic TNFα, IL-1β, caspase-1 and caspase-11 mRNA (normalized to 36B4 mRNA). Data were expressed as fold induction (n=7). Data are expressed as mean±standard error of the mean. Statistical significance from controls is denoted by *,#P≤0.05, **,##P≤0.01, ***,###P≤0.001