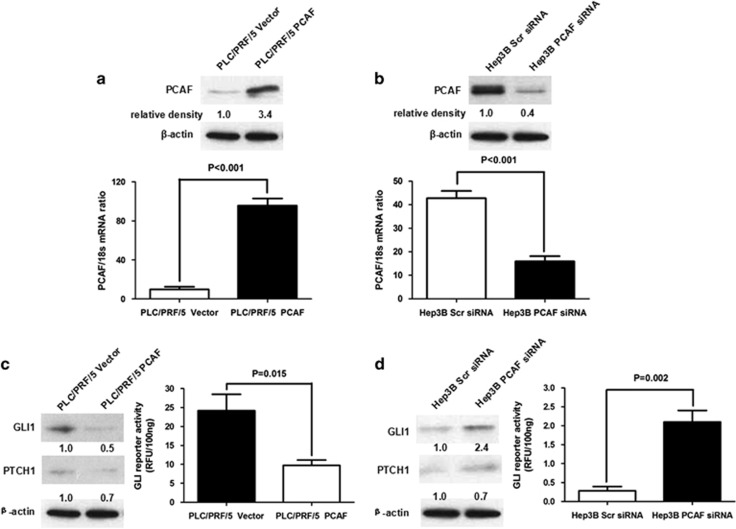
Figure 1.
PCAF repressed the activation of Hh signalling in HCC cell. (a) Plasmids expressing the full-length PCAF mRNA or the control empty were stably transfected into PLC/PRF/5 cells. Compared with PLC/PRF/5 Vector cells, PLC/PRF/5 PCAF cells had significantly higher PCAF expression at the levels of both mRNA and protein. (b) siRNA sequences against PCAF downregulated the mRNA and protein expression of PCAF apparently in Hep3B cells. (c) Enhanced PCAF expression lead to the decrease of expression of both GLI1 and PTCH1 and suppressed GLI-dependent reporter activity in PLC/PRF/5 cells, which indicated that PCAF expression inactivated Hh pathway in HCC cells. (d) Knockdown of PCAF resulted in the upregulation of GLI1 and PTCH1 expression and increased GLI-dependent reporter activity in Hep3B cells. These data demonstrated that aberrant silencing of PCAF lead to the hyperactivation of Hh pathway