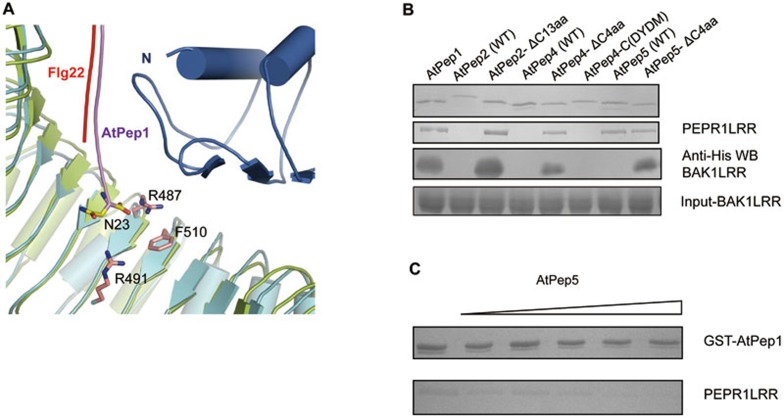
Figure 5.
The C-terminal extensions in AtpPep2,4,5 interfere with PEPR1LRR-BAK1LRR heterodimerization. (A) Extensions at the C-terminal portion of AtPep1 may interfere with PEPR1LRR-BAK1LRR interaction. A close up view of structural comparison between PEPR1LRR-AtPep1 and FLS2LRR-flg22-BAK1LRR around the C-terminal region of AtPep1. The last amino acid AtPep1Asn23 is shown. (B) AtPep2,4,5 with their C-terminal extensions removed induced PEPR1LRR-BAK1LRR interaction. The assay was performed as described in Figure 1A. AtPep4-C(DYDM) represents a mutant AtPep4 with susbstitution of the C-terminal 4 residues of AtPep4 with those of AtPep5. (C) AtPep5 that interacts with PEPR1LRR but fails to induce PEPR1LRR-BAK1LRR interaction inhibits AtPep1-PEPR1LRR interaction. AtPep1 was first mixed with increasing amount of chemically synthesized AtPep5 and then incubated with the PEPR1LRR protein. The mixture was loaded onto GS4B resin. After extensive washing, proteins bound to the GS4B resin were detected by Coomassie blue staining.